Vav Proteins Are Key Regulators of Card9 Signaling for Innate Antifungal Immunity PDF
Preview Vav Proteins Are Key Regulators of Card9 Signaling for Innate Antifungal Immunity
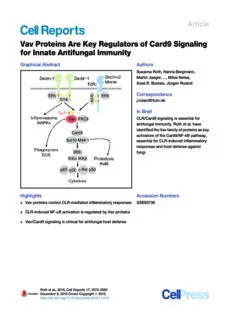
Article Vav Proteins Are Key Regulators of Card9 Signaling for Innate Antifungal Immunity Graphical Abstract Authors SusanneRoth,HannaBergmann, MartinJaeger,...,MihaiNetea, Xose´ R.Bustelo,Ju€rgenRuland Correspondence [email protected] In Brief CLR/Card9signalingisessentialfor antifungalimmunity.Rothetal.have identifiedtheVavfamilyofproteinsaskey activatorsoftheCard9/NF-kBpathway, essentialforCLR-inducedinflammatory responsesandhostdefenseagainst fungi. Highlights Accession Numbers d VavproteinscontrolCLR-mediatedinflammatoryresponses GSE83736 d CLR-inducedNF-kBactivationisregulatedbyVavproteins d Vav/Card9signalingiscriticalforantifungalhostdefense Rothetal.,2016,CellReports17,2572–2583 December6,2016CrownCopyrightª2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.11.018 Cell Reports Article Vav Proteins Are Key Regulators of Card9 Signaling for Innate Antifungal Immunity SusanneRoth,1,2HannaBergmann,1MartinJaeger,3,4AssaYeroslaviz,5KonstantinNeumann,1Paul-AlbertKoenig,1 ClarissaPrazeresdaCosta,6LesleyVanes,7VinodKumar,8MelissaJohnson,9MauricioMenacho-Ma´rquez,10 BiancaHabermann,5VictorL.Tybulewicz,7,11MihaiNetea,3Xose´ R.Bustelo,10,12andJu€rgenRuland1,13,14,15,* 1Institutfu€rKlinischeChemieundPathobiochemie,KlinikumrechtsderIsar,TechnischeUniversita¨tMu€nchen,81675Mu€nchen,Germany 2ChirurgischeKlinik,Universita¨tsklinikumHeidelberg,Ruprecht-Karls-Universita¨t,69120Heidelberg,Germany 3DepartmentofMedicine,RadboudUniversity,MedicalCentre,6500HBNijmegen,theNetherlands 4RadboudCenterforInfectiousDiseases,6500HBNijmegen,theNetherlands 5MaxPlanckInstituteofBiochemistry,ResearchGroupComputationalBiology,82152Martinsried,Germany 6Institutfu€rMedizinischeMikrobiologie,Immunologie,undHygiene,KlinikumrechtsderIsar,TechnischeUniversita¨tMu€nchen, 81675Mu€nchen,Germany 7FrancisCrickInstitute,LondonNW11AT,UK 8DepartmentofGenetics,UniversityMedicalCenterGroningen,UniversityofGroningen,Groningen,9700RB,theNetherlands 9DukeUniversityMedicalCenter,DukeBox102359,Durham,NC27710,USA 10CentrodeInvestigacio´ndelCa´ncer,CSIC-UniversityofSalamanca,37007Salamanca,Spain 11DepartmentofMedicine,ImperialCollege,LondonW120NN,UK 12CentrodeInvestigacionBiomedicaenRed-Oncologia,CarlosIIIHealthInstitute,Spain 13GermanCancerConsortium(DKTK),69120Heidelberg,Germany 14GermanCenterforInfectionResearch(DZIF),PartnerSiteMunich,Munich,Germany 15LeadContact *Correspondence:[email protected] http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.11.018 SUMMARY for host defense and tissue homeostasis (Takeuchi and Akira, 2010).OneimportantfamilyofsignalingPRRsonmyeloidcells Fungalinfectionsaremajorcausesofmorbidityand are the Syk-coupled C-type lectin receptors (Kerrigan and mortality, especially in immunocompromised indi- Brown, 2011; Sancho and Reis e Sousa, 2012). These PRRs viduals. The innate immune system senses fungal playabroadroleininnateimmunityandareparticularlyimpor- pathogensthroughSyk-coupledC-typelectinrecep- tantforhostdefenseagainstfungalinfections(Ferwerdaetal., tors(CLRs),whichsignalthroughtheconservedim- 2009; Robinson et al., 2009; Saijo et al., 2007, 2010; Sato etal.,2006;Tayloretal.,2007;Wellsetal.,2008),whichconsti- mune adaptor Card9. Although Card9 is essential tuteanincreasinghealththreatbecauseofgrowingnumbersof for antifungal defense, the mechanisms that couple patientsatriskmainlybecauseofimmunosuppressivemedical CLR-proximal events to Card9 control are not well interventions and AIDS. In the context of antifungal immunity, defined.Here,weidentifyVavproteinsaskeyactiva- theC-typelectinreceptor(CLR)familymemberDectin-1senses tors of the Card9 pathway. Vav1, Vav2, and Vav3 b-glucans in fungal cell walls (Brown and Gordon, 2001), cooperate downstream of Dectin-1, Dectin-2, and whereas Mincle and Dectin-2 detect a-mannose, glycolipids, MincletoengageCard9forNF-kBcontrolandproin- and a-mannans, respectively (Sancho and Reis e Sousa, flammatory gene transcription. Although Vav family 2012).AgonistbindingbyDectin-1leadstothephosphorylation members show functional redundancy, Vav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1) of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-like mice phenocopy Card9(cid:1)/(cid:1) animals with extreme motifsin its cytoplasmictail bySrc family kinases,resulting in susceptibilitytofungi.Inthiscontext,Vav3isthesin- activation of the tyrosine kinase Syk. Likewise, Dectin-2 and Mincle also activate Syk, indicating that these CLR signals glemostimportantVavinmice,andapolymorphism in human VAV3 is associated with susceptibility to engagecommoneffectormechanisms(Mo´csaietal.,2010;San- choandReiseSousa,2012).Theinnateimmuneadaptorprotein candidemiainpatients.Ourresultsrevealamolecu- Card9iscriticalforCLRsignaling.Itassemblessignalingcom- lar mechanism for CLR-mediated Card9 regulation plexes that also contain Bcl10 and Malt1 (Card9-BCl10-Malt1 thatcontrolsinnateimmunitytofungalinfections. [CBM]complexes)andthatserveasscaffoldsforactivationof thecanonicalnuclearfactorkB(NF-kB)pathway(RothandRu- INTRODUCTION land,2013).ThismechanismactivatestheinhibitorofkappaB (IkB) kinase (IKK) complex, which phosphorylates inhibitory Cellsoftheinnateimmunesystemsensemicrobialcomponents IkBs,leadingtotheirproteasomaldegradationandtherelease or cell damage-associated structures via germline-encoded of NF-kB dimers to the nucleus to activate gene transcription pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that subsequently signal (VallabhapurapuandKarin,2009).Malt1canalsofunctionasa 2572 CellReports17,2572–2583,December6,2016CrownCopyrightª2016 ThisisanopenaccessarticleundertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/). protease upon CBM complex assembly that cleaves a set of bySrcandSykkinases(Bustelo,2014).Todeterminetheimpor- NF-kB regulators, including RelB, to fine-tune immune gene tanceoftheCLR-proximalSrcandSykkinasesinVavphosphor- expression(Hailfingeretal.,2011;Jaworskietal.,2014).These ylation,wepretreatedBMDCswiththeSrcinhibitorPP2orthe Card9 signaling complexes operate downstream of all tested SykinhibitorR406priortotheadditionofC.albicans.BothSrc Syk-coupled CLRs (Roth and Ruland, 2013) and are essential and Syk inhibition blocked Vav1-Tyr174 phosphorylation in for innate antifungal immunity. Indeed, Card9-deficient mice adose-dependentmanner,whereaspretreatmentwithPP3,an are highly susceptible to infection with Candida (Gross et al., inactiveanalogofPP2,didnotaffectC.albicans-inducedphos- 2006; Jia et al., 2014), Aspergillus (Jhingran et al., 2012), and phorylationofVav1atTyr174(Figure1C).Together,theseresults Cryptococcus (Yamamoto et al., 2014) species. Moreover, indicate that Vav1 is activated in myeloid antigen-presenting loss-of-function mutationsinhuman CARD9havebeenidenti- cells specifically after fungal sensing via an Src and Syk ki- fiedascausesofmucocutaneousandinvasivefungalinfections nase-dependentmechanism. (Glockeretal.,2009;Pe´rezdeDiegoetal.,2015).Nevertheless, despite the critical role for CLR-triggered Card9 signaling in CLR-MediatedInflammatoryResponsesAreCritically innate immunity and mammalian host defense, the molecular DependentonVavProteins mechanismsthatlinkCLRligationtoCard9-dependenteffector Next, we studied the functional relevance of Vav proteins in mechanismsarenotwellunderstood. C.albicans-inducedinflammatoryresponses.Becausedendritic Here, we used a mass spectrometry-based proteomic cellsexpressVav2(Spurrelletal.,2009)inadditiontoVav1and approach and identified Vav proteins as regulators of Card9 Vav3,whichhavepartiallyredundantfunctionsinimmunecells signaling. Vav1, Vav2, and Vav3 cooperate downstream of (Fujikawa et al., 2003; Tybulewicz, 2005), we investigated Dectin-1,Dectin-2,andMincletoengageCard9complexesfor BMDCs from mice that lack each individual Vav isoform, two NF-kB control and proinflammatory gene transcription. Like Vav isoforms, or all three Vav family members. Notably, the Card9-deficientmice,Vav1/2/3triple-deficientmiceareseverely lackofanyoneorallVavmoleculesdidnotimpairBMDCdiffer- impairedininflammatoryresponsestoCandidaalbicansinfec- entiation (data not shown; Graham et al., 2007; Spurrell et al., tionandhostdefenseagainstthefungus.Moreover,wereport 2009). However, BMDCs from Vav1/2/3 triple-deficient mice ahumanpolymorphisminVAV3thatisassociatedwithsuscep- wereseverelydefectiveinC.albicans-inducedTNFproduction, tibilitytocandidemia.Thus,ourresultsestablishVavproteinsas whereas tumor necrosis factor (TNF) secretion in response to essential regulators of CLR-mediated Card9 control in innate Toll-like receptor (TLR) stimulation with LPS or Pam3CSK4 antifungalimmunity. wasunaffectedinthesecells(Figure2A).Moreover,theproduc- tionofinterleukin-2(IL-2)andIL-10wasalsodefectiveinBMDCs RESULTS fromVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)mice(Figure2A).ThefindingthatVav1,Vav2, orVav3single-deficientorVav2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)myeloidantigen-present- FungalInfectionInducesTyrosinePhosphorylationof ingcellsareonlypartiallyimpairedinC.albicans-inducedTNF, VavinMyeloidCells IL-2,andIL-10generation(Figure2B)indicatesredundancyfor ToinvestigatethemechanismsofSyk-coupledCLRsignaling,we Vavproteinsinfungus-inducedcytokineresponses. stimulatedwild-typemurinebonemarrow-deriveddendriticcells Oneimportantinflammatorycytokineforantifungalimmunity (BMDCs), comprisingconventional DCs and monocyte-derived isIL-1b(Vonketal.,2006),thegenerationofwhichiscontrolled macrophages(Helftetal.,2015),for10minwithzymosan,ayeast by NF-kB-dependent pro-IL-1b gene transcription followed by cellwallpreparationthatishighlyenrichedinDectin-1andDec- NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated Caspase-1-dependent pro- tin-2agonists,andsubsequentlyaffinity-purifiedtyrosine-phos- IL-1bprocessing(Grossetal.,2009;Hiseetal.,2009).Stimula- phorylated proteins for mass spectrometric analysis (Strasser tion of wild-type BMDCs with C. albicans induced the robust etal.,2012).Undertheseconditions,weobservedsignal-induced secretionofmatureIL-1bintotheculturesupernatant(Figure2C). tyrosinephosphorylationofVav1andVav3,whicharecytosolic In contrast, Vav1/2/3-deficient cells were almost completely signaling scaffolds and guanine nucleotide exchange factors defective in Candida-induced IL-1b production (Figure 2C). thatcanplaycontext-specificrolesinimmunereceptorpathways Thisdefectwascausedbytheselectiveimpairmentofpro-IL- (Bustelo,2014).Tovalidatethesefindings,westimulatedBMDCs 1bgenetranscriptioninVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)cells(Figure2D),whereas withC.albicanshyphaeandspecificallyanalyzedVav1phosphor- thedeficiencyof Vavproteins didnotaffectNLRP3inflamma- ylationbywesternblotanalysis.Indeed,Vav1wastyrosine-phos- some-dependent Caspase-1 activation (Figure 2E). Together, phorylatedafterC.albicansinfection(Figure1A).Thesedataarein these experiments demonstrate that Vav proteins are critical linewithpreviouslypublishedresultsthatdemonstratedthatstim- forcytokineproductionbymyeloidcellsfollowingthedetection ulationwithb-glucanorzymosantriggerstyrosinephosphoryla- ofwholefungalcells. tionofVav1alsoinmicroglialcellsorneutrophils(Lietal.,2011; Next,westudiedthespecificrequirementofVavproteinsfor Shah et al., 2009). Further analysis with a phosphospecific Dectin-1-, Dectin-2-, and Mincle-induced cytokine responses antibody raised against the regulatory Tyr174 residue of Vav1 usingselectiveagonistsforeachindividualreceptor.Stimulation additionallyrevealedthatthisspecificresidueisphosphorylated of Dectin-1 with curdlan, a purified particulate b-glucan (Lei- uponC.albicansdetection,indicatingVav1activation(Aghazadeh bundGut-Landmannetal.,2007),inducedtherobustproduction etal.,2000),butnotuponLPSstimulation(Figure1B). of TNF in wild-type BMDCs, whereas Vav1/2/3-deficient Recent work has demonstrated that Vav phosphorylation cells failed to produce TNF in response to Dectin-1 triggering downstreamofdifferentITAM-containingreceptorsismediated (Figure 2F). Likewise, stimulation of BMDCs with agonistic CellReports17,2572–2583,December6,2016 2573 A B C Figure1. Vav1IsTyrosine-PhosphorylatedinResponsetoCandida (A)BMDCswereuntreated((cid:1))orstimulatedwithC.albicanshyphae(MOI5)for15min.Proteinsfromcelllysateswereimmunopurifiedwithanti-phospho- tyrosineantibodiesandanalyzedbyimmunoblotwithaVav1antibody(left).AlsoshownisquantificationofVav1bydensitometry(right). (B)ImmunoblotanalysisofBMDCsunstimulated((cid:1)),treatedwithC.albicanshyphae(MOI0.5)fortheindicatedtimes,orstimulatedwithLPS(100ng/ml)for 45minandprobedwithantibodiesagainstphospho-Vav1(Tyr174)orVav1(left).Alsoshownisdensitometricalquantificationofphospho-Vav1relativetototal Vav1,normalizedtoBMDCstreatedwithC.albicansfor45min(right). (C)BMDCswereuntreated((cid:1))orpreincubatedwiththeSykinhibitorR406(0.5,1,and2mM)ortheSrc-kinaseinhibitorPP2(1.5,3,and6mM)oritsinactiveanalog PP3(1.5,3,and6mM)andthenstimulatedwithC.albicanshyphae(MOI1)for30min.Lysateswereimmunoblottedwithanti-phospho-Vav1(Tyr174)oranti-Vav1 antibodies(left).Alsoshownisdensitometricalquantificationofphospho-Vav1relativetototalVav1,normalizedtoBMDCstreatedwithC.albicanswithoutany inhibitors(right).Dataofatleastthreeindependentexperimentsareshownasmean±SEM. *p<0.05,**p<0.01,***p<0.001;Student’sttest(A)andone-wayANOVAandposthocTukey-Kramertest(C).n.s.,notsignificant. antibodies against Dectin-2 or with trehalose-6,6-dibehenate Mincle ligand TDM (Ishikawa et al., 2009; Miyake et al., 2013) (TDB),asyntheticanalogofthemycobacterialcordfactortreha- intowild-typeandVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)mice.Consistentwithpreviously lose6,60-dimycolate(TDM),whichspecificallyactivatesMincle publishedresults(Ishikawaetal.,2009),TDMinjectionresulted (Lobato-Pascual et al., 2013; Miyake et al., 2013; Schoenen in the strong systemic production of TNF, IL-1b, and IL-10 in etal.,2010),inducedTNFinwild-typecells,butthisresponse wild-type mice (Figure 2H). However, these responses were wasseverelyimpairedinVav1/2/3-deficientBMDCs(Figure2F). defectiveinVav1/2/3triple-deficientanimals(Figure2H).Next, Therefore,althoughVavsingle-ordouble-mutantcellsexhibited westudiedtheroleofVavproteinsininflammatorycytokinere- apartiallyimpairedcytokineresponseuponselectiveDectin-1, sponses after fungal infection in vivo. To this end, we intrave- Dectin-2,orMinclestimulation(Figure2G),theVavfamilyasa nouslyinjectedwild-typeorVav1/2/3tripleknockoutmicewith whole is essential for cytokine production after Syk-coupled liveC.albicansandmeasuredserumTNFandIL-6levelsafter CLRligationinvitro. 6 hr. Notably, the production of both inflammatory cytokines was almost completely abolished in Vav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1) mice (Fig- VavProteinsRegulateCLR-InducedInflammatory ure3A).Subsequently,westudiedtheimportanceofindividual ResponsesInVivoandAreEssentialforAntifungal Vavproteins in hostprotection against fungi byinfecting wild- Defense type or Vav single-, double-, or triple-deficient mice with 1 3 To investigate the function of Vav proteins in CLR-mediated 105colony-formingunits(CFUs)ofC.albicans.Fourdayslater, inflammatory responses in vivo, we intravenously injected the we assessed intravital fungal growth in the kidneys, the main 2574 CellReports17,2572–2583,December6,2016 A B C D E F G H Figure2. VavProteinsAreEssentialforSyk-CoupledCLR-InducedProinflammatoryResponses (AandB)TNF,IL-2,andIL-10levelsinthesupernatantsofwild-type(WT)andVav1/2/3-/-BMDCs(A),orVavsingle-ordoublemutantBMDCsoftheindicated genotypes(B)thatwereuntreated((cid:1))orstimulatedwithC.albicanshyphae(MOI0.3),LPS(500ng/ml),orPam3CSK4(50ng/ml)for16hrwereanalyzedbyELISA. (C)IL-1binthesupernatantsofWTandVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)BMDCsleftuntreated((cid:1))orstimulatedwithC.albicanshyphae(MOI1)for6hr. (D)Quantitativereal-timePCRanalysisofIL-1btranscriptsinWTandVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)BMDCsleftuntreatedorstimulatedwithC.albicanshyphae(MOI1)(left)orLPS (100ng/ml)(right)fortheindicatedtimes;resultsarerelativetothoseofb-actinmRNA. (E)ImmunoblotanalysisofmatureCaspase-1(p10)incellculturesupernatantsofWTandVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)((cid:1)/(cid:1))BMDCsleftuntreated((cid:1)),stimulatedwithC.albicans hyphae(MOI1)for4hr(C.a.),orpre-stimulatedwithLPS(50ng/ml)for6hrpriortotheadditionofATP(5mM)for45min(A+L).QuantificationofmatureCaspase-1 p10bydensitometryisshowntotherightofthewesternblot. (legendcontinuedonnextpage) CellReports17,2572–2583,December6,2016 2575 target organ of the fungus (Brieland et al., 2001). Although and S1B), this response is almost completely abolished in the wild-type mice cleared the fungus readily, the kidneys of all absenceofVavproteins(Figure4C;FigureS1A)orPKCd(Fig- investigated Vav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1) mice were enlarged and infiltrated ureS1B;Strasseretal.,2012).Consistentwiththesefindings, withmacroscopicallyvisiblefungalcolonies(Figure3B).Quanti- C.albicans-inducednucleartranslocationofthetranscriptional tatively, we detected more than 100-fold higher titers of activeNF-kBsubunitsp65,c-Rel,andRelBwerealsoseverely C. albicans in the kidneys of Vav1/2/3 triple-deficient animals defectiveinVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)BMDCs,astheyareinCard9-deficient compared with the wild-type (Figure 3C), and histopathology cells(Figures4Dand4E;FiguresS1CandS1D),demonstratinga confirmed intravital fungal growth (Figure 3D). The fungal bur- criticalroleforVavproteinsinCLR-dependentNF-kBcontrol. dens in Vav3 single knockout and Vav2/3 double knockout As indicatedabove, the activation of the Card9/Bcl10/Malt1 mice were increased by trend compared with the wild-type, complex not only regulates IKK activation but also induces butaselectivelossofVav1orVav2didnotresultinhigherfungal Malt1 proteolytic activity (Jaworski et al., 2014). Consistently, titerscomparedwithwild-typemice(Figure3C).Finally,westud- stimulationofwild-typeBMDCswithCLRligandsresultsinthe iedtheroleofVavsignalinginthesurvivalofmiceafterfungal rapidproteolyticprocessingoftheMalt1substrateRelB(Figures infection. In line with the incapacity to control fungal invasion 4Fand4G;FiguresS1EandS1F;Gewiesetal.,2014;Hailfinger oftheorgans,Vav1/2/3-deficientmicediedrapidlyafterinjection etal.,2011;Jaworskietal.,2014).Curdlan-inducedRelBcleav- of13105CFUofC.albicans,whereasthewild-typecontrolan- agewascompletelydefectiveinBMDCsfromMalt1(cid:1)/(cid:1)miceand imals survived this challenge (Figure 3E). These experiments frommicewithgene-targetedinactivationoftheMalt1paracas- reveal that Vavproteins play essential roles in fungus-induced pase function (Malt1PM/(cid:1)) (Gewies et al., 2014; Figure 4F; Fig- cytokineproductionandantifungalimmunityinvivo,withVav3 ure S1E) and, therefore, can be used as a marker for CBM beingthesinglemostimportantVavfamilymemberforprotec- complex activation. Likewise, Malt1-mediated RelB cleavage tionagainstC.albicansinfection. uponC.albicansstimulationwasalsodefectiveinVav1/2/3triple knockout cells (Figure 4G; Figure S1F), which, together with VavProteinsAreRegulatorsofCLR-InducedNF-kB the defective IKK activation in Vav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1) BMDCs, indicates Activation that Vav proteins operate upstream of the Card9/Bcl10/Malt1 The susceptibility of Vav1/2/3 triple-deficient animals and the signalosome. failuretoinduceCLR-mediatedcytokineresponsesarereminis- Finally, we studied the role of Vav proteins in CLR-induced centoftheseverephenotypeobservedinCard9-deficientmice, geneexpressioninaglobalmanner.Tothisend,weperformed suggestingthatVavproteinsandCard9mayoperateinacom- high-throughput cDNA sequencing (RNA sequencing [RNA- mon signaling cascade. Because of the partially overlapping seq]) followed bygene setenrichment analysis (GSEA) of cur- functions of the three Vav isoforms, we focused subsequent dlan-stimulated and untreated BMDCs. In Dectin-1-stimulated biochemical studies on Vav1/2/3 triple knockout BMDCs. wild-typeBMDCs,wedetectedasignificantenrichmentofupre- UponC.albicansstimulation,phosphorylationofthetyrosineki- gulated NF-kB-dependent transcripts compared with Vav1/ naseSykandoftheDectin-1signaltransducerPLCg2(Xuetal., 2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1) cells (Figure 4H), which isconsistent with the defective 2009)didnotdifferbetweenwild-typeandVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)BMDCs IKK activation described above. These results further validate (Figure 4A), indicating that Vav proteins are not required for Vav proteins as essential regulators of CLR-mediated NF-kB the immediate receptor-proximal events. Moreover, because control. Erk1/2, p38, and Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) were similarly phosphorylated in C. albicans-stimulated wild-type and Vav1/ AHumanVav3PolymorphismIsAssociatedwith 2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)BMDCs(Figure4B),weconcludethatVavsarenotessen- SusceptibilitytoCandidemia tialfortheregulationofmitogen-activatedproteinkinase(MAPK) AfteridentifyingVavproteinsasintegralregulatorsoftheDec- signalingafterfungalinfection.However,activationofproteinki- tin-1/Card9/NF-kB signaling cascade in murine cells, we were nase C d (PKCd), which controls Card9 engagement (Strasser interestedinthepotentialrolesforVavmoleculesinhumananti- etal.,2012),waspartiallyimpairedinBMDCslackingallthree fungalimmunity.Therefore,weinvestigatedwhethergeneticvar- Vavisoforms(Figure4C;FigureS1A).Likewise,PKCddeficiency iationslinkedtoanyoftheVAVgenescorrelatewithsusceptibility partially compromised Vav1 phosphorylation in response to to candidemia in patients by studying a previously described C. albicans or curdlan stimulation (Figure S1B). Moreover, cohortofcandidemiapatientsandanappropriatecontrolgroup althoughC.albicansorcurdlanstimulationofwild-typeBMDCs (Jaegeretal.,2015).Interestingly,theanalysisofSNPsassoci- inducestherapidactivationoftheIKKcomplex,asdetermined atedwithVAV3revealedasignificantassociationwithcandide- by measuring IKKa/bphosphorylation (Figure 4C;Figures S1A mia, with the significant SNPs distributed across the linkage (FandG)BMDCsfromWTandVav1/2/3-/-mice(F),orVavsingle-ordoublemutantmiceoftheindicatedgenotypes(G)wereuntreated((cid:1)),stimulatedwiththe Dectin-1ligandcurdlan(10mg/ml),plate-boundanti-Dectin-2(12.5mg/ml)orisotypecontrolantibodies(Isotype),ortheMincleligandTDB(100mg/ml).TNFlevels inthecellculturesupernatantswerequantifiedbyELISA. (H)WTandVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)micewereinjectedintravenouslywithTDMcontainingoil-in-wateremulsionsorwiththevehiclecontrol((cid:1)).24hrpost-injection,TNF, IL-1b,andIL-10levelsinseraweredeterminedbyCBA. (A,B,F,andG)DataareexpressedaspercentofWT±SEMofthreeindependentexperiments. (C–EandH)Dataofatleastthreeindependentexperimentsarepresentedasmean±SEM. *p<0.05,**p<0.01,and***p<0.001,Student’sttest(A,C,F,andH),andone-wayANOVAandposthocTukey-Kramertest(BandG). 2576 CellReports17,2572–2583,December6,2016 A B C D E Figure3. VavProteinsAreRequiredforSystemicAntifungalHostDefense (A–E)Miceoftheindicatedgenotypeswereintravenouslyinfectedwith13105CFUsofC.albicans. (A)SerumIL-6andTNFlevelsinWTandVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)miceweredeterminedbyCBA6hrafterinfection. (BandC)After4days,kidneysweremacroscopicallyexamined(B;scalebar,10mm),andC.albicanstitersweredeterminedinthekidneys(C). (D)KidneysectionsfromC.albicans-infectedWTandVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)micewerestainedwithH&Eorperiodicacid-Schiff(PAS;scalebars,100mm). (E)WT(n=5)andVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)(n=4)miceweremonitoreddailyforhealthandsurvival.Statisticalsurvivalanalyseswereperformedusingthelog-ranktest (p<0.005). (AandC)Eachsymbolrepresentsanindividualmouse;smallhorizontallinesindicatethemean;errorbarsindicatetheSEM.Dataofoneexperimentineachcase arepresented.*p<0.05,Student’sttest(AandC,left)andone-wayANOVA(C,right,p=0.06). disequilibrium(LD)regionofthegene.Theassociationdoesnot dependent NF-kB activation similar to Card9 deficiency, with extend beyond the LD region, and the strongest association Vav3beingthemostimportantfamilymemberinthispathway waswiththeSNPrs4914950(Figure5A).Theriskgenotypeof inmiceand,presumably,inhumans. theSNPrs4914950TTisincreasedfrom10%(controlpopulation) When engaged by fungal particles, Syk-coupled CLRs acti- to18%(candidemiapatients)(Figure5B). vate various intracellular signaling pathways that regulate phagocytosis, microbicidal activities, and gene transcription. DISCUSSION Using C. albicans as a clinically relevant model organism that issensedbymultipleCLRsandinducesCLRsignaling(Robin- Using a complementary approach of immunology, molecular son et al., 2009; Taylor et al., 2007; Wells et al., 2008), we biology,andgeneticstudies,theresultspresentedinthismanu- observedVavactivationdownstreamofSyk.Inaddition,using scriptdefineanessentialroleforVavproteinsinCLR-mediated defined agonists of Dectin-1, Dectin-2, and Mincle, we estab- inflammatory responses and establish these molecules as lishedageneralroleforVavproteinsinCLRsignalinginmyeloid essential signaling platforms that relay proximal events from antigen-presenting cells. However, our results that CLR-medi- Syk-coupled CLRs to the Card9 signaling complex for NF-kB ated MAPK activation and inflammasome signaling are not control and antifungal defense (Dambuza and Brown, 2015; impairedinVav1/2/3triple-deficientBMDCsrevealthatVavpro- Osorio and Reis e Sousa, 2011; Roth and Ruland, 2013). teins only mediate specific CLR effector mechanisms. Recent Although individual Vav isoforms can compensate for each studies have indicated the involvement of Vav1 and Vav3 in other, their combined absence results in a blockade of CLR- Dectin-1-mediatedzymosanphagocytosisandreactiveoxygen CellReports17,2572–2583,December6,2016 2577 A B C D E H F G Figure4. VavProteinsControlCLR-TriggeredNF-kBActivation (A–E)BMDCsfromtheindicatedgenotypeswerestimulatedwithC.albicanshyphae(MOI0.5)forvarioustimesorwithLPS(100ng/ml)for45min. (A)SykandPLCg2phosphorylationwasdeterminedincelllysatesbyimmunoblotwithanti-phospho-Sykandanti-phospho-PLCg2antibodies. (B)ActivationoftheMAPkinasesErk1/2,p38,andJNKwasanalyzedwithanti-phospho-Erk1/2,anti-phospho-p38,andanti-phospho-JNKantibodies. (C)Celllysateswereanalyzedbyimmunoblotwithanti-phospho-PKCdandanti-phospho-IKKa/bantibodies.b-actinservedasaloadingcontrol. (DandE)NuclearextractsfromWTandVav1/2/3-/-(D),orCard9-/-BMDCs(E)wereanalyzedbyimmunoblotwithantibodiesagainsttheNF-kBsubunitsp65, c-Rel,andRelB;anti-laminBantibodiesindicateequalproteinloading. (legendcontinuedonnextpage) 2578 CellReports17,2572–2583,December6,2016 species(ROS)productioninneutrophilsandtherecruitmentof dependence of these mechanisms should be defined in the Vav1tophagocyticcupsforC.albicansengulfmentbymacro- future. phages (Li et al., 2011; Strijbis et al., 2013). Although these Inaccordancewithourmolecularmodel,similartoCard9defi- effector mechanisms are important during innate immune re- ciency, a complete deficiency in all Vav isoforms results in a sponses,theyarenotregulatedbytheCard9pathway(Drewniak massivesusceptibilitytoC.albicansinfection.Likewise,acondi- etal.,2013;Goodridgeetal.,2009;Grossetal.,2006).However, tional deficiency of Syk only in dendritic cells also abolishes theCard9signalingpathwayappearstobethecentralmamma- innateresistancetoacutesystemicC.albicansinfection(Whit- lianhostdefensemechanismagainstfungi,giventhatmultiple ney et al., 2014), and Whitney et al. (2014) elegantly demon- geneticstudiesinhumanshaverecentlyidentifiedthatseveral strated that the early innate cytokine response is required to Card9loss-of-functiondefectsarecausativeforseveralfungal orchestrate innate anti-fungal functions, including neutrophil diseases, including various types of mucocutaneous candidi- anti-fungal activity. Nevertheless, in our infection models pre- asis;superficial,extensive,anddeepdermatophytosiswithTri- sentedhere,itmustbenotedthattheVavmutantmiceanalyzed chophyton spp.; subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis; invasive were germline Vav-deficient animals and thatVav proteins are Candidainfectionsofthedigestivetractandcentralnervoussys- not selectively expressed in Syk and Card9-containing innate tem;Candidaendophthalmitisandosteomyelitis;anddissemi- immunecells,includingdendriticcells,macrophages,andneu- natedExophialadiseaseoftheliver,brain,andlung(Grumach trophils, but are also expressed in lymphocytes, which signal etal.,2015;Pe´rezdeDiegoetal.,2015). through Card9-independent mechanisms (Gross et al., 2006; WeassessedenzymaticMalt1paracaspaseactivityasadirect Hara et al.,2007). Still, the rapid deathof Vav1/2/3 triple-defi- functional marker for Card9 complex activity in Vav-deficient cientmiceuponfungalinfectionindicatesthataninnateimmune mice.GiventhatthisactivitywasseverelyimpairedinVav1/2/3 defectisindeed responsible forthe observedphenotype. This triple-deficientBMDCs,ourresultsestablishVavmoleculesas hypothesisisalsoinlinewiththeestablishedrolesofVav1and regulators of the Card9/Bcl10/Malt1 complex. Consistent with Vav3inmediatingphagocytosisandROSproductioninmacro- theessentialfunctionofaVav/Card9-mediatedmechanismfor phagesandneutrophilsuponfungalsensing(Lietal.,2011;Strij- CLR-inducedNF-kBactivation,theNF-kBresponseisblocked bisetal.,2013).FuturestudieswithconditionalVavmutantmice in Vav1/2/3-deficient mice in response to C. albicans infection will further dissect the individual roles of Vav signaling in den- or selective CLR triggering, and Vav1/2/3-deficient animals driticcells,macrophages,andneutrophilsaswellasinadaptive exhibitdramaticallyimpairedproinflammatorycytokineproduc- immune subsets during complex fungal infection scenarios tion in response to C. albicans infection and CLR stimulation in vivo. In addition, in vivo results in individual Vav1-, 2-, invitroandinvivo.Therefore,weproposeamechanisticmodel and 3-deficient animals also revealed that, although there is inwhichSykisengagedbyCLRsuponfungalsensing,thereby functionalredundancyamongthethreeVavfamilymembersin triggering the phosphorylation and activation of Vav proteins, infection control, Vav3 is the single most important Vav family whichsubsequentlyactivatetheCard9complexforNF-kBcon- memberforantifungaldefenseinmice.Thisfindingisconsistent trolandantifungalgenetranscription. withourresultsinpatientswholinkapolymorphismintheVAV3 HowVavproteinsaremechanisticallycoupledtoCard9con- genetosusceptibilitytoCandidainfection,suggestingthatthe trol remains to be determined. We previously demonstrated functionofVavmoleculesissimilartoCard9functionconserved that Card9 is phosphorylated by PKCd at Thr231 to induce betweenmiceandmen. Card9 effector function. However, the activation of PKCd is Inadditiontofungalcomponents,CLRsalsorecognizestruc- only partially impaired in Vav-deficient BMDCs, whereas IKK tures present on mycobacteria (Ishikawa et al., 2009; Lobato- activation is almost completely defective. Similarly, in PKCd- Pascualetal.,2013;Miyakeetal.,2013;Schoenenetal.,2010), deficientcells,IKKphosphorylationisabolished,whereasphos- virusessuchasdenguevirus(Chenetal.,2008),andparasites phorylation of Vav1 is only slightly compromised, suggesting, such as Schistosoma mansoni (Ritter et al., 2010), as well as together,thatVavandPKCdoperateatthesamelevelupstream endogenousligandsundersterileinflammatoryconditions(Roth ofCard9.BecauseVavproteinscancontrolcytoskeletalreorga- andRuland,2013).Wethereforebelievethatourfindingshave nization and serve as scaffolding platforms in other signaling implicationsbeyondantifungalimmunity.Consistentwiththishy- systems (Acton et al., 2012; Bustelo, 2014; Spurrell et al., pothesis,Vav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)micewerealmostcompletelyimpairedin 2009;Tybulewicz,2005),wespeculatethatVavfamilymembers systemicinflammatoryresponsesuponinnateimmunestimula- could bring Card9 into the vicinity of key upstream regulators tionwiththemycobacterialpathogen-associatedmolecularpat- such as PKCd and potential, still unknown factors to allow terns (PAMP) analog TDM, implying that, like Card9 (Dorhoi Card9activation.Moreover,becauseVav1/2/3donotonlyregu- etal., 2010), Vavproteinsmight alsobe criticalforinnateanti- lateCLR-inducedCard9-NF-kBsignalingbutalsocontrolother mycobacterialimmuneresponses.Inaddition,accumulatingevi- cellularresponses,suchasphagocytosisandROSproduction denceindicatesimportantrolesforCLR/Card9signalingininflam- (Lietal.,2011;Strijbisetal.,2013),theprecisemolecularinter- matory disorders. Several independent studies have shown an (FandG)BMDCsfrommiceoftheindicatedgenotypeswerepretreatedwiththeproteasomeinhibitorMG132for30minandthenstimulatedwithcurdlan (0.5mg/ml)(F)orC.albicanshyphae(MOI1)(G)for2or4hr.CelllysateswereanalyzedbyimmunoblotusingantibodiesagainstRelBandb-actin. (H)WTandVav1/2/3(cid:1)/(cid:1)BMDCswerestimulatedwithcurdlan(0.2mg/ml)for3hr.ShownistheGSEAenrichmentscoreofNF-kBtargetgenesdifferentially expressedincurdlan-stimulatedwild-typecellscomparedwithVav1/2/3-deficientBMDCs. Dataarerepresentativeofatleastthreeindependentexperiments.SeealsoFigureS1. CellReports17,2572–2583,December6,2016 2579 A B Figure5. AVAV3PolymorphismIsAssociatedwithIncreasedSusceptibilitytoCandidemia (A)Polymorphismsassociatedwithcandidemiawereinvestigatedinagroupof227patientswithCandida-positivebloodculturesandcomparedwith176 patientsfromthesameclinicalwardswithoutinfection.SNPsassociatedwiththeVAV3locusrevealedasignificantassociationwithcandidemia,withthe significantSNPsdistributedacrosstheLDregionofthegene.TheVAV3generegiononchromosome1isshown.UsingtheSNAPserver,theSNPofinterest (rs4914950)(biggestorangediamond)wasplottedwithallannotatedpolymorphismsinthisgene(otherdiamonds).R2andrecombinationrateareindicatedon theleftandrightyaxis,respectively.DiamondsonthesamehorizontallineastheSNPofinterest(biggestorangediamond)areincompletelinkagedisequilibrium (R2=1)withthisSNPandhavethesamediseaseassociationvalues.DiamondsbelowthislinehavealowerLDvaluewiththeSNPofinterestand,therefore,differ intheassociationwiththedisease.Thetablebelowshowsthetop15polymorphismsthatarelinkedtors4914950. (B)Genotypefrequenciesforthers4914950SNPthatshowedthestrongestassociationwithcandidemia.Thetablebelowshowsthetotalnumbersandper- centages(inparentheses)ofgenotypesinCandida-infected(candidemiapatients)andnon-infected(controls)individuals.Statisticalcomparisonsofgenotype frequenciesbetweenthetwogroupsweremadeusingc2test. associationbetweenCard9polymorphismsandulcerativecolitis nephropathy(Kiryluketal.,2014).Inconjunctionwiththeresults and Crohn’s disease (Roth and Ruland, 2013), which are sup- presented here, these data suggest that the described Vav/ portedbyarecentstudyinmicedemonstratingaprotectiverole Card9-dependentsignalingmechanismcouldalsoplayarolein forCard9inintestinalinflammation(Sokoletal.,2013).Deepre- sterileinflammatorydiseases. sequencingofinflammatoryboweldiseasegenome-wideassoci- ationstudy(GWAS)lociconfirmedanassociationbetweenCard9 EXPERIMENTALPROCEDURES andulcerativecolitisandCrohn’sdisease(Beaudoinetal.,2013; Hongetal.,2016).Moreover,additionalgenome-wideassociation Mice studies in humans have identified significant associations be- Vav1(cid:1)/(cid:1)(Turneretal.,1997),Vav2(cid:1)/(cid:1)(Doodyetal.,2001),Vav3(cid:1)/(cid:1)(Sauzeau tweenCARD9andVAV3genelociandimmunoglobulinA(IgA) etal.,2006),Card9(cid:1)/(cid:1)(Grossetal.,2006),Prkcd(cid:1)/(cid:1)(Leitgesetal.,2001), 2580 CellReports17,2572–2583,December6,2016
Description: