NASA Technical Reports Server (NTRS) 20120015028: Observations of C-Band Brightness Temperature from the Hurricane Imaging Radiometer (HIRAD) on Board NASA WB-57 During GRIP in Hurricanes Earl And Karl (2010) PDF
Preview NASA Technical Reports Server (NTRS) 20120015028: Observations of C-Band Brightness Temperature from the Hurricane Imaging Radiometer (HIRAD) on Board NASA WB-57 During GRIP in Hurricanes Earl And Karl (2010)
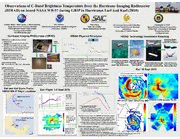
Observations of C-Band Brightness Temperature from the Hurricane Imaging Radiometer (HIRAD) on board NASA WB-57 during GRIP in Hurricanes Earl And Karl (2010) Timothy Miller*, Mark James, J. Brent Roberts, Eric Uhlhorn Peter Black W. Linwood Jones and Cathy May Christopher S. Ruf# Sayak Biswas and Courtney Buckley Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological SAIC, Inc at NRL/ Central Florida Remote Sensing Space Physics Research Laboratory, NASA Marshall Space Flight Center Laboratory (AOML) Marine Meteorology Division Laboratory AOSS Dept., University of Michigan *Corresponding Author University of Central Florida #Presenting Author [email protected] [email protected] Hurricane Imaging RADiometer (HIRAD) HIRAD Physical Principles HIRAD Technology Investment Roadmap HIRAD Passive Microwave C-Band Technology Transfer: • RVeardsiioomn e1t:eHr :-pol at 4, 5, 6 & 6.6 GHz HVeIRrsAioDn 1 •SimiGlarRS twIo PNa At(h2S0 AG1 H0eSo)3 mH GeIlRotrbAyal DH awk CyOclpoenrea tRioencaoln Tnroapisiscaanlc e configuration for 2012-2014 • freqfor wind speed and rain rate Version 2:H-& V-pol continuum of C- band freqfor Ocean Surface Vector Wind (OSVW) & rain rate ••PerEfaorrtmha Inncceid Cenhcaera acntegrleis:t 0ic-s6:0°, HVeIRrsAioDn 2 • Spatial Resolution: 2-5 km, • Swath: ~70 km for 20 km altitude HIRAD measures ‘emissivity’ over a range of incidence angles and frequencies from ocean surface foam (a function of wind Operational use of SFMR for HIRAD first flight-2010: WObSs: e1r0v atoti o>n8a5l mG/osa; l sR:R: 2 to > 100 mm/hr •sAwpti neCde-d-bd)a ranivnded nm i nficoteraormvwe iansv iienn gfvr arearqiiaunne. tn wciieths f(r4e-6q.u6e GncHyz )w, ehmileis rsaiivniftayl lf rom (OAcFe WaCna -S1nu3dr0f aRJc,a Nein OW RAainAtde W SpP-e3eDd) NARSaAPp riGodjR eIInPct-te (GnWseiBfni-ce5as7ti)sio ann d mNSiesesxvito eunrp e2: 0 SN1toA2r-Sm1A4 S H(eGunrltroiincbeaaln l( eHH aSa3wn)dk ) OWIcmienpadrons vaSeundrdf a HRcuaerirn iVc Reaacntteeo r H•IREAxDp aanddvsa nScteepsp:ed Frequency •eTmheisssei vpihtyy sisic aa ls ctrhoanrgac ftuenricsttiiocns oafl lforweq tuweon cgye.ophysical variables Karl 16 Sept 2010 Microwave Radiometer (SFMR) • (wind speed and rain rate) to be derived from emissivity • cEsoalimvmepirnlaiangtgee s fwr SoiFmthM nwRai ddmeira- sxtow w waitnihdd es u asnmwdpaeltrih-ng Atmh oacrnoe n4 at idcnicusuucrmraet teoe f w ofrinneedqs us wepnielcle irdee ssr eurtalrtti heinev ar ls •mdmeeatatehsremumrienametidec’na, lt‘ lstee aactsh t4n--si6qq udueiassrce.rse’t per Cob-bleamnd s forelvqaubelen cwieitsh, caonn ‘ovevnerti-onal P-3R caodmarp;o +si tHeI cReAnDte; r+ ti mWein ~d2 0C:e4n4t eUrTsC 60 60 0 -60 • of entire eyewall(instantaneously) and with dual-polarization: wind Surface wind speed and rain rate retrievals are derived from Uses synthetic thinned array and RFI • direction retrievals as well (OSVW). empirical correlation of HIRAD measured emissivity at mitigation technology of Lightweight It will also eliminate wind and rain operating incidence angles with co-located GPS dropsonde Rain Radiometer (NASA Instrument retrieval ambiguities in gale-force surface wind observations and accepted functional relations Storm track Incubator) wind regimes. for rain attenuation vsfrequency. 0 Earl and Karl Storm Tracks: Karl 16 Sept Center Position Earl Flight: 1-2 Sept 2010 19.84 HIRAD WB-57 Flight Locations 19.82 P3 reported 180 WEST - 4&5 GHz HIRAD Tb@ 4GHz HP3IR raAdDar ssuubbjjeeccttiivvee 19.8 HIRHADu frlirghitcane Earl Tb (K)111246000 WS (kt) HMMIooRddAeeDll TTTbbb@@@ 455GGGHHHzzz 111999...777468 WP-3DP LartFia l rouatedr acornc ernetrficl eeycewtailvlity dBZ-60HIRAD 5 GHz excess Tb (K) Sept Aug RR (mm/hr)13001 0468 00000 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80531000 c“SSMoFFmMMoRRdp eWuRlati”neinddd ++ a5f5tr(00am(o k( (mmmtam)rm// hseS/)rh F)Tr)Mb’Rs ••GWaoPno-d3d D Wa gwPri-en3edDm cLeeFnn trt eabrdesat wrcoecenenns itsHetrIesRnAtlDy south 111999...67782 118200WBt-r5a7c fklight wind & rain fields of LF radarand HIRADcenters as seen in radar composite image to right 19.66 -94.1 -94 -93.9 -93.8 -93.7 -93.6 -93.5 -93.4 -93.3 19.64 60 HIRAD 4-and Key features of radar and HIRAD comparison (right): Hurricane Karl 5-GHz observed 1) EyewalldBZand HIRAD Tb maxima are located in left- Tb values agree front quadrant. This, together with open eyewallin right- HIRAD flights SFMR with SFMR Tb rear quadrant, suggest easterly environmental shear. 0 values 2) Partial outer concentric eyewallis suggested equally well in radar and HIRAD images, as is outer principal rainband. -60 HIRAD GRIP Calibration Challenges Best day • Rain rate and wind speed retrievals to be based on three calibrated frequencies: SFMR HWSFIBRM-A5RD7 o aobtb s2s0ffr-rokommm ; •HI5CR aGAliHDbz rca Tatibloib(nMr aoictfir ooontwh iaesvrs eu2 e Bcsrh iaagnnhdntn emelssit siisg T aientmi opnpro sf)go hrre aHsvSse;3 b:ceoemnp sleutciocens wsfituhlliyn p3r modounctheds -120 120 60 0 -60 -120 Calibration uses internal reference blackbody targets and noise diodes Sept WP-3D at 3 km TCeamlibpreartaiotunr ea lcgoorrritehcmtio dne aplegnodrsit homn rbeefienrge ndceev eTlbo:p uendc oforrr eGcRteIdP i(nresqtruuimreesn atd tdemitipoenraal tiunrset rduempeenntd cehnacrea fcotuernidza dtiuornin tge sGtiRnIgP) flights (+/-25oC) Thermal control subsystem has been upgraded for HS3 to minimize instrument temperature fluctuations
