B.Sc. (Physics) PDF
Preview B.Sc. (Physics)
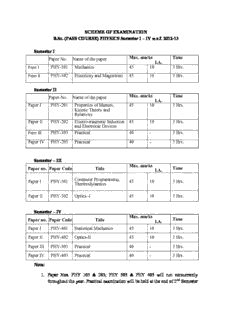
SCHEME OF EXAMINATION B.Sc. (PASS COURSE) PHYSICS Semester I – IV w.e.f. 2012-13 Semester I Max. marks Time Paper No. Name of the paper I.A. Paper I PHY-101 Mechanics 45 10 3 Hrs. Paper II PHY-102 Electricity and Magnetism 45 10 3 Hrs. Semester II Max. marks Time Paper-No. Name of the paper I.A. Paper I PHY-201 Properties of Matters, 45 10 3 Hrs. Kinetic Theory and Relativity Paper II PHY-202 Electro-magnetic Induction 45 10 3 Hrs. and Electronic Devices Paper III PHY-103 Practical 40 - 3 Hrs. Paper IV PHY-203 Practical 40 - 3 Hrs. Semester – III Max. marks Paper no. Paper Code Title Time I.A. Computer Programming, Paper I PHY-301 45 10 3 Hrs. Thermodynamics Paper II PHY-302 Optics -I 45 10 3 Hrs. Semester – IV Max. marks Paper no. Paper Code Title Time I.A. Paper I PHY-401 Statistical Mechanics 45 10 3 Hrs. Paper II PHY-402 Optics-II 45 10 3 Hrs. Paper III PHY-303 Practical 40 - 3 Hrs. Paper IV PHY-403 Practical 40 - 3 Hrs. Note: 1. Paper Nos. PHY 103 & 203; PHY 303 & PHY 403 will run concurrently throughout the year. Practical examination will be held at the end of 2nd Semester (for PHY 103 & PHY 203) and 4th Semester (for PHY-303 & PHY 403). The work load for practical is 3 periods / week/ practical paper. 2. One Practical from each paper is to be performed in the practical examination. INTERNAL ASSESSMENT :-The Internal Assessment for theory papers comprises of (i) Attendance- 2.50 (ii) Unscheduled test 2.50 (iii)Assignments- 5.00 Total 10 B.Sc. PHYSICS SCHEME OF EXAMINATION Semester-I Paper I- PHY 101 : MECHANICS Max. Marks : 45 Internal Assessment : 10 Time : 3 Hrs. NOTE : 1. The syllabus is divided into 3 units. Eight questions will be set up. At least two questions will be set from each unit and the student will have to attempt at least one question from each unit. A student has to attempt five question in all. 2. 20% numerical problems are to be set. 3. Use of Scientific (non-programmable) calculator is allowed. Unit I Mechanics of single and system of particles, conservation of laws of linear momentum, angular momentum and mechanical energy, Centre of mass and equation of motion, constrained motion, degrees of freedom. Unit II Generalised coordinates, displacement, velocity, acceleration, momentum, force and potential. Hamilton’s variational principle , Lagrange’s equation of motion from Hamilton’s Principle. Linear Harmonic oscillator, simple pendulum, Atwood’s machine. Unit III Rotation of Rigid body, noment of inertia, torque, angular momentum, kinetic energy of rotation. Theorems of perpendicular and parallel axes with proof. Moment of inertia of solid sphere, hollow sphere, spherical shell, solid cylinder, hollow cylinder and solid bar of rectangular cross-section. Acceleration of a body rolling down on an inclined plane. References 1. Classical Mechanics by V.K.Jain (Ane 2009) 2. Classical Mechanics by H. Goldstein (2nd Edition) 3. Berkeley Physics Course, Vol. I, Mechanics by E.M. Purchell B.Sc. PHYSICS Paper II- PHY 102 : ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Max. Marks : 45 Internal Assessment : 10 Time : 3 Hrs. NOTE : 1. The syllabus is divided into 3 units. Eight questions will be set up. At least two questions will be set from each unit and the student will have to attempt at least one question from each unit. A student has to attempt five question in all. 2. 20% numerical problems are to be set. 3. Use of Scientific (non-programmable) calculator is allowed. Unit I Mathematical Background : Scalars and Vectors, dot and cross product, Triple vector product, Scalar and Vector fields, Differentiation of a vector, Gradient of a scalar and its physical significance, Integration of a vector (line, surface and volume integral and their physical significance), Gauss’s divergence theorem and Stocks theorem. Electrostatic Field : Derivation of field E from potential as gradient, derivation of Laplace and Poisson equations. Elecotric flux, Gauss’s Law and its application to spherical shell, uniformly charged infinite plane and uniformity charged straight wire, mechanical force of charged surface, Energy per unit volume. Unit II Magnetostatistics : Magnetic Induction, magetic flux, solenoidal nature of Vector field of induction. Properties of B (i) .B = 0 (ii) xB= J. Electronic theory of dia and para magnetism (Langevin’s theory). Domain theory of ferromagnetism. Cycle of Magnetisation - Hysteresis (Energy dissipation, Hysteresis loss and importance of Hysteresis curve). Unit III Electromagnetic Theory : Maxwell equation and their derivations, Displacement Current. Vector and scalar potentials, boundary conditions at interface between two different media, Propagation of electromagnetic wave (Basic idea, no derivation). Poynting vector and Poynting theorem. References : 1. Electricity and Magnetism by Reitz and Milford (Prentice Hall of India) 2. Electricity and Magnetism by A.S. Mahajan and A.A. Rangwala (Tata McGraw Hill). B.Sc. PHYSICS Paper III Phy- 103 PRACTICALS Max. Marks : 40 Time : 3 Hrs. SPECIAL NOTES 1. Do any eight experiments . 2. The students are required to calculate the error involved in a particular experiment (percentage error). NOTE 1. Distribution of Marks : Experiment : = 20 marks Viva Voce : = 10 marks Lab Record : = 10 marks Total = 40 marks For giving marks under Lab. Record each college will maintain practical assessment record by using the following procedure :- 1. Each student has to peform a minimum number of experiments prescribed in the syllabus. 2. After the completion of a practical the teacher concerned will check the note- book and conduct the viva-voce of each student to find out how much concepts related to the theoertical and experimental part of the experiment he/she has understood. According to his/her performance marks will be recorded in their practical note book. These marks will constitue the lab record. 3. To complete the final marks for lab. record a separate register for each class of B.Sc will be maintained. The Student will be assigned a separate page on the register. On this page the marks obtained by the student in different practicals will be recorded. While taking the final average the total marks obtained willbe divided by the total no. of required practicals, instead of the number of practicals performed by the student. This record will be signed by the concerned teacher. 4. The lab. record register will be presented to the external practical examiners for lab. record marks. The external examiners will verify the record randomly. B.Sc. PHYSICS Paper III- PHY 103 PRACTICALS Max. Marks : 40 Time : 3 Hours 1. Moment of Inertia of a fly-wheel 2. M.I. of an irregular body using a torsion pendulum. 3. Surface Tension by Jeager’s method. 4. Young’s modulus by bending of beam. 5. Modulus of rigidity by Maxwell’s needle. 6. Elastic constants by Searle’s method. 7. Viscosity of water by its flow through a uniform capillary tube. 8. Thermal conductivity of a good conductor by Searle’s method. 9. Mechanical equivalent of Heat by Callendao and Barne’s method. 10. ‘g’ by Bar pendulum. B.Sc. PHYSICS SCHEME OF EXAMINATION Semester-II Paper I- PHY 201 : PROPERTIES OF MATTER, KINETIC THEORY AND RELATIVITY Max. Marks : 45 Internal Assessment : 10 Time : 3 Hrs. NOTE : 1. The syllabus is divided into 3 units. Eight questions will be set up. At least two questions will be set from each unit and the student will have to attempt at least one question from each unit. A student has to attempt five question in all. 2. 20% numerical problems are to be set. 3. Use of Scientific (non-programmable) calculator is allowed. Unit - I Properties of Matter (Elasticity) : Elasticity, Hooke’s law, Elastic constants and their relations, Poisson’s ratio, torsion of cylinder and twisting couple. Bending of beam (bending moment and its magnitude) cantilevers, Centrally loaded beam. Unit - II Kinetic Theory of Gases : Assumptions of Kinetic Theory of gases, Law of equipartition of energy and its applications for specific heats of gases. Maxwell distribution of speeds and velocities (derivation required), Experiomental verification of Maxwell’s Law of speed distribution : most probable speed, average and r.m.s. speed, mean free path. Transport of energy and momentum, diffusion of gases. Brownian motion (qualitative), Real gases, Van der Waal’s equation. Unit - III Theory of Relativity : Reference systems, inertial frames, Gallilean invariance and Conservation laws, Newtonian relativity principle, Michelson - Morley experiment : Search for ether. Lorentz transformations length contraction, time dilation, velocity addition theorem, variation of mass with velocity and mass energy equivalence. References 1. Properties of Matter by D.S. Mathur. 2. Heat and Thermodynamics (Vth Edition) by Mark W. Zemansky. 3. Berkeley Physics Course, Vol.-I Mechanics by E.M. Purchell. B.Sc. PHYSICS Paper II- PHY 202 : ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ELECTRONIC DEVICES Max. Marks : 45 Internal Assessment : 10 Time : 3 Hrs. NOTE : 1. The syllabus is divided into 3 units. Eight questions will be set up. At least two questions will be set from each unit and the student will have to attempt at least one question from each unit. A student has to attempt five question in all. 2. 20% numerical problems are to be set. 3. Use of Scientific (non-programmable) calculator is allowed. Unit I Electromagnetic Induction :Growth and decay of current in a circuit with (a) Capacitance and resistance (b) resistance and inductance (c) Capacitance and inductance (d) Capacitance resistance and inductance. AC circuit analysis using complex variables with (a) capacitance and resistance, (b) resistance and inductance (c) capacitance and inductance (d) capacitance, inductance and resistance Series and parallel resonant circuit. Quality factor (Sharpness of resonance). Unit II Semiconductor Diodes : Energy bands in solids. Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor, Hall effect, P-N junction diode and their V-I characteristics. Zener and avalanche breakdown. Resistance of a diode, Light Emitting diodes (LED). Photo conduction in semiconductors, photodiode, Solar Cell. Diode Rectifiers :P-N junction half wave and full wave rectifier. Types of filter circuits (L and-with theory). Zener diode as voltage regulator, simple regulated power supply. Transistors :Junction Transistors, Bipolar transistors, working of NPN and PNP transistors, Transistor connections (C-B, C-E, C-C mode), constants of transistor. Transistor characteristic curves (excluding h parameter analysis), advantage of C-B configuration. C.R. O. (Principle, construction and working in detail). Unit III Transistor Amplifers : Transistor biasing, methods of Transistor biasing and stabilization. D.C. load line. Common-base and common-emitter transistor biasing. Common-base, common- emitteer amplifers. Classification of amplifers. Resistance-capacitance (R-C) coupledamplifer (two stage; concept of band width, no derivation). Feed-back in amplifers, advantage of negative feedback Emitter follower. Oscillators : Oscillators, Principle of Oscillation, Classification of Oscillator. Condition for self sustained oscillation : Barkhousen Criterion for oscillations. Tuned collector common emitter oscillator. Hartley oscillator. Colpitt’s oscillator. References : 1. Electricity and Magnetism by Reitz and Milford (Prentice Hall of India) 2. Electricity and Magnetismby A.S. Mahajan and A.A. Rangwala (Tata McGraw Hill). 3. Basic Electronics and Linear circuits by N.N. Bhargava, D.C. Kulshreshtha and S.C. Gupta (TITI, CHD). 4. Soild State Electronics by J.P. Agarwal, Amit Agarwal (Pragati Prakashan, Meerut). 5. Electronic Fundamentals and Applications by J.D. Ryder (Prentice Hall India). B.Sc. PHYSICS Paper III Phy- 203 PRACTICALS Max. Marks : 40 Time : 3 Hrs. SPECIAL NOTES 1. Do any eight experiments . 2. The students are required to calculate the error involved in a particular experiment (percentage error). NOTE 1. Distribution of Marks : Experiment : = 20 marks Viva Voce : = 10 marks Lab Record : = 10 marks Total = 40 marks For giving marks under Lab. Record each college will maintain practical assessment record by using the following procedure :- 1. Each student has to peform a minimum number of experiments prescribed in the syllabus. 2. After the completion of a practical the teacher concerned will check the note- book and conduct the viva-voce of each student to find out how much concepts related to the theoertical and experimental part of the experiment he/she has understood. According to his/her performance marks will be recorded in their practical note book. These marks will constitue the lab record. 3. To complete the final marks for lab. record a separate register for each class of B.Sc will be maintained. The Student will be assigned a separate page on the register. On this page the marks obtained by the student in different practicals will be recorded. While taking the final average the total marks obtained willbe divided by the total no. of required practicals, instead of the number of practicals performed by the student. This record will be signed by the concerned teacher. 4. The lab. record register will be presented to the external practical examiners for lab. record marks. The external examiners will verify the record randomly. B.Sc. PHYSICS Paper III- PHY 203 PRACTICALS Max. Marks : 40 Time : 3 Hours 1. E.C.E. of hydrogen using an Ammeter. 2. Calibration of thermocouple by potentiometer. 3. Low resistance by Carey Foster’s Bridge with calibration. 4. Determination of impendance of an A.C. circuit and its verification. 5. Frequency of A.C. mains and capacity by elctrical vibrator. 6. Frequency of A.C. mains by sonometer using an electromagnet. 7. Measurement of angle dip by earth inductor. 8. High resistance by substitution method. 9. Inductance (L) by Anderson Bridge (A.C. method) 10. To draw forward and reverse bias characteristics of a semiconductor diode. 11. Zener Doide volage regulation characteristics. 12. Verification of Inverse square law by photo-cell. 13. To study the characteristics of a solar cell.
Description: