AMBASSADOR FRANÇOIS M. DICKMAN - Association for PDF
Preview AMBASSADOR FRANÇOIS M. DICKMAN - Association for
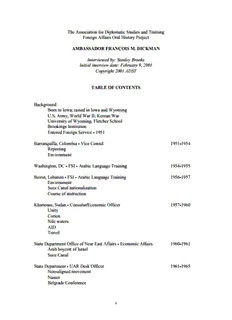
The Association for Diplomatic Studies and Training Foreign Affairs Oral History Project AMBASSADOR FRANÇOIS M. DICKMAN Interviewed by: Stanley Brooks Initial interview date: February 9, 2001 Copyright 2001 ADST TABLE OF CONTENTS Background Born in Iowa; raised in Iowa and Wyoming U.S. Army, World War II; Korean War University of Wyoming; Fletcher School Brookings Institution Entered Foreign Service - 1951 Barranquilla, Colombia - Vice Consul 1951-1954 Reporting Environment Washington, DC - FSI - Arabic Language Training 1954-1955 Beirut, Lebanon - FSI - Arabic Language Training 1956-1957 Environment Suez Canal nationalization Course of instruction Khartoum, Sudan - Consular/Economic Officer 1957-1960 Unity Cotton Nile waters AID Travel State Department Office of Near East Affairs - Economic Affairs 1960-1961 Arab boycott of Israel Suez Canal State Department - UAR Desk Officer 1961-1965 Non-aligned movement Nasser Belgrade Conference 1 Syria-Egypt union ends U.S. missiles to Israel PL 480 for Egypt North Yemen-Egypt Yemen Republicans Egyptian-Saudi relations Egypt’s missiles Dimona CANE (Control of Arms Near East) McCloy Middle East missions Abu Simbel USIS Cairo library burned Syria Margaret’s activities Tunis, Tunisia - Economic officer 1965-1968 French Nationalization Economy PL 480 AID Arab-Israel 1967 war Embassy attacked President Bourguiba Environment Margaret’s activities Army War College (Carlisle, Pennsylvania) 1968-1969 Jeddah, Saudi Arabia - Economic/Political Officer 1969-1972 Environment Jidda-Riyadh “shuttle” Deterrent Force North Yemen ARAMCO OPEC Shah of Iran London Group Military equipment Joseph Kraft Arabists Oman Desalination plant State Department - Arabian Peninsula - Country Director 1972-1976 Arab Emirates 2 Gulf States PDRY Persian Gulf Iran Saudi-U.S. investments Secretary of State Rogers’ Yemen visit Congressional interest Moore-Noel assassinations Black September Arms sales Natural gas Yom Kippur 1973 war Oil embargo French-Japanese tactics Congressional interest Washington Energy Conference International Energy Agency U.S.-Saudi Joint Economic Commission (JECOR) Yamani King Faisal assassinated U.S. ambassadors to Gulf States Oman U.S. Gulf bases Israel boycott Ambassador James Akins Kuwait liaison office Abu Dhabi - Ambassador 1976-1979 Oil pricing Tax Reform Act - 1976 Gulf states rulers Political developments Economy Egypt-Israel treaty Arms sales Kuwait - Ambassador 1979-1983 Teheran embassy seizure Kuwait Future Generations Fund Security alerts A.R. Aliqi Evacuation Population Palestine issue Press Moscow Olympics 3 Camp David negotiations U.S.-Kuwait relations Gulf Cooperation Council Iraq-Kuwait relations Kuwait Fund for Economic Development Oil pricing OPEC Iraq-Iran war Women’s suffrage Shia minority Voting Sabah family Abu Ain case Palestinian community Kristine Olman case Kuwaiti-U.S. investments Kuwait Petroleum Company Sante Fe International purchase Lebanon Secretary of State Shultz’s shuttle Stock market crash Marquette University - Diplomat in Residence 1983-1984 Kuwait bombing reports Retirement - University of Wyoming 1984 Adjunct professor Observation: Iraq-Iran INTERVIEW Q: Today is February 9, 2001. This is an interview with Ambassador François M. Dickman in his home in Laramie, Wyoming on behalf of The Association for Diplomatic Studies and Training. I’m Stanley Brooks, a retired Foreign Service officer who has also chosen to retire in Wyoming. Ambassador Dickman, how is it that someone who grew up in Wyoming found himself in the Foreign Service? DICKMAN: Well, let me give you a little bit of background. First of all, I was born in Iowa City in 1924. I came to Laramie in 1933 after my father was appointed as the head of the Modern Language Department at the University of Wyoming. Both my parents were language teachers. My father was born in Antwerp, Belgium. He survived World War I after six years in the Belgian army. After being demobilized in 1919, he came to the U.S. at the invitation of an older brother who was living in Waco, Texas and who was a cotton broker. But my father soon realized that he wasn’t cut out for the cotton 4 business, so he got his master’s degree in French and German at Baylor. My mother was born in Tarbes, a city in the southern part of France. She came to the United States in 1920 as an exchange student at Millikin University in Decatur, Illinois. She had previously taught English in a French lycée. Although she had every intention of returning to France (I think she got a degree after one year at Millikin), she was offered a job as a French instructor in Baylor in 1921. It is there in Waco that my parents met. My father got his M.A. at Baylor and then got a job to teach at the University of Iowa. So, my parents moved to Iowa City. There, my father obtained his Ph.D. at the University of Iowa in 1925. I think they went to Iowa about 1923 or thereabouts because I was born in Iowa City. My father remained an associate professor in the Modern Language Department until 1932 when he was appointed to be the chair or the head of the Language Department at the University of Wyoming. I should also point out that I am an only child. Since French was spoken at home, I was raised bilingually. Of course, with both parents coming from Europe, world events were constantly discussed at home. My father had a passionate hatred for the Germans, which wasn’t surprising since he had barely survived as an infantryman during his six years in the Belgian army. On several occasions during the trench warfare, he had been buried alive. He suffered from a bullet hole through his upper calf. Although he recovered from poison gas attacks, it resulted in a lifetime of psoriasis causing him to have red blotches all over his skin. He used to treat these blotches with Lysol. I don’t know why Lysol, but that’s what he used. Of course, my parents were very concerned with the rise of Hitler. My father spoke German fluently. I can recall vividly my father shouting back in German during Hitler’s radio broadcasts warning everyone who was willing to listen of the growing German danger and the need to treat “Mein Kampf” seriously. He would say, “Hitler has spelled it all out. We know exactly what his ideas are.” He quite correctly anticipated that Germany under Hitler would renew its war against Britain and France and that the Germans would invade Belgium using the Schlieffen Plan just like they did in 1914. In fact, when the war broke out, my father told me that he first entered combat at Liege where his unit tried to fend off the German advance and actually managed to delay the advance for a few days. As I recall, the Belgian army finally had to retreat to the Yser River, which is right on the French-Belgian border. That’s where a static line was established for the rest of the war and where my father spent the rest of the war in the trenches. As for my mother, she was the intellectual in the family and did most of the work on the language textbooks that my parents prepared. My mother identified with and was very tied emotionally to her native France. Every three years, my parents would make a trip to Europe to visit my grandparents. The visits that I remember the best were the ones in 1935 when I was 10 and in 1938 when I was 13. At that time, it was possible to load the family car at quite a reasonable price on the transatlantic ship. This meant driving from Laramie to New York City, which took four or five days, and then taking the car to the dock to be loaded on the ship. Once you reached Le Havre, the car was unloaded and we just hopped in and that was it. 5 In 1938, we took the Normandie, which was a magnificent vessel. Even though we traveled third class, which was the cheapest class, it was a very comfortable trip. In 1938, for example, when we visited France, we drove to Boulogne, where my mother had an uncle and aunt. On this occasion, my father left my mother and me to stay with the uncle and aunt while he drove the family car to Belgium to visit an old friend of his, an academic at the University of Liege. The two took the occasion to make a brief visit into Germany where they witnessed the construction of the autobahns. I recall my father saying that these superhighways were all directed toward the French and Belgian borders. Since there was very little German traffic, he thought it was obvious what they were going to be used for military purposes. After my father returned from his trip to Belgium and Germany, we drove to Paris and then south to Tarbes to visit my grandfather on my mothers’ side. During that summer, accompanied by my grandfather, we all traveled in the family car to Italy, first to Genoa and then down to Rome. It was in August of 1938. What I recall vividly was the fact that Hitler had just made his visit to Italy. Everywhere along the highways, you could see the signs “Duce, Duce, Duce” painted along the highways. The other favorite sign on many buildings was the proclamation “Obedire, Credere, Combatere,” in other words, “Obey, Believe, and Fight.” After Rome, we visited Florence, Sienna, and Venice and then drove back to France. On our way back to the United States, we stopped in Saint Malo to visit friends who were later killed during the war. The discussion centered on the German threat and a statement U.S. Ambassador William Bullitt had made which seemed to imply that the U.S. was concerned by the German threat. By the time we had returned to the U.S., we learned of the trip by Prime Ministers Chamberlain and Daladier to Munich. My parents were convinced that World War II was going to start shortly, particularly with Hitler pressing Poland to relinquish the Danzig Corridor. I recall in Wyoming, as a High School, student attending a speech at the University given by a Polish diplomat on the Danzig Corridor and the threats that were being posed by Germany. The problem was that people in Wyoming were not concerned about this. The visit to Europe in the summer of 1938 had only redoubled my parents’ concerns about the imminence of another world war, which isolationist Americans were indifferent to, especially in a landlocked state like Wyoming. So, to answer your question, it’s little wonder that early in life I was aware of events in the world, particularly in Europe, and I’m sure it influenced my interest in making the Foreign Service my career goal. I remember obtaining a pamphlet on the Foreign Service issued, I think, in 1939, which explained the details of the career. In the back, there was a sample examination. I recall studying those questions very carefully and wondering if I would ever pass the test. Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbor ended the isolationist period of America. My father eagerly volunteered his services to the U.S. Army. In October of 1942, he was commissioned as a Captain in military intelligence. I should have pointed out earlier that both my parents had become naturalized American citizens. My father was sent to North Africa in early 1943. He served initially as an American liaison officer with the Second 6 Moroccan Division, which saw action in Italy, including Monte Cassino. Then he was attached to the Third Algerian Division, which participated in the 1944 invasion of southern France and remained as the liaison officer with the Third Algerian as it proceeded north into Luxembourg, Germany, and Austria. He ended up with five battle stars. Q. What about your military service? DICKMAN: As for myself, I was drafted in July 1943 at the age of 18. I had five months of basic infantry training at Fort Benning. This was when the ASTP [Army Specialized Training Program] was still underway. After basic training, I was sent to Princeton in January 1944 for language training. There, I was told the only language courses that were available were Turkish or Arabic. At the time, I had no idea which to choose because I was totally unfamiliar with the Middle East. I flipped a coin and it came out Turkish. Because the ASTP program also included area studies, one of the classes at Princeton was given by Professor Hitti. Through his lectures, I became aware of the issues revolving around the future of Palestine. I should point out that my stay in Princeton was short-lived. By March 1944, the ASTP program was disbanded because of manpower needs to fill a new infantry division. While I was in Princeton, we were given language tests. As a result, I ended up in Camp Ritchie, Maryland for training in military intelligence for a French interrogation team. However, I never got to Europe. Because the armored breakthrough in France in the summer of 1944 had been so successful, there was no longer any need for French interrogation teams. So, I became, if you will, a retread. I was given lengthy training to become a member of the 46th Japanese Order of Battle Team which was activated on May 16, 1945. It consisted of one officer, a senior non- commissioned officer (me), and one junior non-commissioned officer. We were given Japanese language training but depended on a Nisei to serve as interpreter and translate documents. Our team was sent to the Philippines where we teamed up with Sergeant Kazuo Ibara. There I learned that our team was scheduled to be attached to one of two regimental combat teams that were to be part of the first wave to land on the island of Kyushu in early November 1945. I have no doubt that the decision to use the A bomb saved my life and that of many others. I don’t have any doubt about that. With Japan’s surrender, I left the Philippines on a troop ship and landed in Wakayama, Japan on September 15, 1945. I might point out that Wakayama was a port city in southeastern Honshu that had been flattened by a single raid of incendiaries. But we did not stay in Wakayama. We ended up in Kyoto, the ancient capital of Japan, where I spent nearly five months in occupation duty. Kyoto was the headquarters of the Sixth Army under General Krueger. Thankfully, Kyoto had not been touched by the war. The time spent in Japan was devoted almost entirely to the preparation of a report on all the Japanese military units which fell under the Sixth Army’s zone of responsibility. The report indicated where the units had been located, the names of the principal officers, and 7 their status. This was important for historical reasons as well as to make sure that all these units had been demobilized and their weapons had been stored. In December 1945, I had the opportunity to make a brief visit to Hiroshima. Comparing it to Wakayama, I could not tell the difference between a city that had been destroyed by a single raid of incendiaries and one wiped out by a single bomb. But what impressed me was the awesome destruction that Japan had been subjected to by our air force and what it might have been like if the Emperor had refused to surrender. In February 1946, the Sixth Army headquarters was moved back to the U.S.; our Order of Battle Team was disbanded. I sailed from Nagoya, impressed by the fact that I could already see thousands of houses that had been burned to the ground being already in the early stages of construction. I was impressed by the resilience of the Japanese people. Upon reaching the U.S., I was demobilized and returned to Laramie at the end of the month to resume my studies at the University of Wyoming and take advantage of the GI bill. At that time, the University had a quarter rather than a semester system so that it was very easy to register for entry in the third quarter of the year. I should point out that before being drafted, I had entered the University of Wyoming in 1942. By taking courses when I was a senior in high school in 1941 and then taking courses in summer school, I had managed to earn over two years of university credit. This enabled me to graduate on June 2, 1947. The following day, I married Margaret Hoy. We had met on the campus and had been engaged for a year. Margaret was born and raised in Cheyenne. She had graduated from the University of Wyoming the year before, majoring in home economics. In order to be close by until our marriage a year later, Margaret had given up the chance to be an intern at the Henry Ford hospital in Detroit in diet therapy. Instead, she took a job teaching food and nutrition at the junior high school in Cheyenne. At the time, I thought that home economics had little relation to my interest in international affairs, but I would learn later that I could not have been more mistaken. I found out through Margaret’s volunteer activities that food and society were very relevant in every country where we served. Since everyone is interested in food and how it’s prepared, it’s a subject that always evokes interest in other societies. By the time of my graduation from the University of Wyoming, I had gained admission to the Fletcher School of Law and Diplomacy at Tufts University. In 1948, I received my Master of Arts at Fletcher. But I continued my studies there with the expectation of obtaining a doctoral degree. The excellent education that I received at Fletcher was far superior to any of the classes that I had had at the University of Wyoming. My favorite professors were Ruhl Bartlett, who taught American diplomatic history, and Nicodemus Halm, who taught comparative economic systems and international finance. Professor Halm gave the best explanation I ever heard of Marxism and its weaknesses. Leo Gross taught international law. Paul Samuelson taught international trade. Samuelson as a teacher was not nearly as good as his basic economic textbook. But it was at Fletcher that I discovered that I had a real interest in international political economy. In particular, I 8 was fascinated by the ideas of John Maynard Keynes, the British economist. Curiously, when I had taken a class in economics at the University of Wyoming, the professor never mentioned Keynes. It was after my first year at Fletcher that I passed the written Foreign Service Exam. My score was 72, which was barely above the passing mark was 70. I realized that I would never have succeeded in passing the four day exam had I not attended the Fletcher School. In March 1949, I traveled to Washington, DC to take the oral exam. I passed and I was exhilarated at the prospect of entering the Foreign Service after completing my Ph.D. orals at Fletcher. By this time, budgetary stringencies were putting Foreign Service entrants on hold. At one point, I was told that there was a waiting list and I happened to be 141st on the waiting list. In September of 1949, I passed the Ph.D. orals at Fletcher and started working on my thesis. The thesis focused on U.S. post-war economic assistance in Europe. By April 1950, my GI Bill had run out, so I was looking for a job. Of course, the thesis wasn’t finished yet. But thanks to the connections of one of my professors at the Fletcher School, I was hired as a research assistant at the Brookings Institution in Washington, DC for a salary of then $5,000 a year, which was a very generous salary. I worked with Leo Pasvolski, who had been very much involved with the creation of the United Nations; Redverse Opie, who was an Oxford Don; and William Adams Brown. It was on a project that focused on economic aid provided by the United States to Western Europe and areas occupied by the U.S. after the war. What was interesting was that it was very much in line with the Ph.D. thesis that I was preparing. My expectation was that I would work at Brookings for a year or so until my turn to enter the Foreign Service would come up. However, it didn’t work out that way. Two days after our daughter, Christine, was born (in Arlington, Virginia, on June 23, 1950), North Korea invaded South Korea. Upon being demobilized after World War II, I had signed up to remain in the inactive enlisted reserves in military intelligence with my non- commissioned rank of tech sergeant. But the reservists were the first to be called up as the Pentagon sought to have a rapid buildup of our armed forces. So, I was sent to Fort Campbell, Kentucky for basic infantry training. My military occupation specialty had been changed from military intelligence to reconnaissance platoon sergeant. I should mention that the training was an eye opener of how ill-prepared we were for this conflict. For example, we were initially issued only one set of fatigues. Each squad was allowed to fire only one bazooka shell. The same for the 60mm mortar. The training lasted six or seven weeks. Once it was over, I was very lucky not to be sent to Korea. By this time, a bureaucratic decision had been made to not send the first two ranks of non-commissioned officers to Korea in order to keep these ratings open for those already in the field. So, I ended up in Fort Bragg, where I was assigned to a finance unit. Margaret did not join me but remained in the small apartment we had rented in Virginia to take care of the baby. With the outbreak of the Korean War, the State Department all of a sudden had money. So, I received a letter shortly after I returned to military service offering me entry as an FS-06. Actually, they were looking for Kreis officers at that time to go to Germany. I 9 asked if the Department could help facilitate my entry into the Foreign Service, but I was told, no, they were not going to intervene. “But you’ll get priority when you get out” is the way they put it. In fact, this is what occurred. After being demobilized for a second time at the end of August 1951, I entered the Foreign Service on October 9, 1951, two and a half years after passing the oral exam. I soon learned that the Department had very cleverly delayed the entry of this Foreign Service class by a couple of weeks to avoid the nine months of service needed for time in grade promotion. Q: So, finally, you’re in the Foreign Service. What was your first posting? DICKMAN: After three months of indoctrination at the Foreign Service Institute, I was told my assignment would be as vice consul in our consulate in Barranquilla, Colombia. I should admit that this was not my choice of area. I had assumed one reason for the assignment to Barranquilla was my knowledge of Spanish. I had minored in Spanish at the university and I guess I was reasonably fluent in it. But what I discovered was that another officer in the entering class had managed to avoid this posting, but for another reason. I learned the reason why. Vice consuls assigned to Colombia were denied diplomatic privileges for the entry of their cars. So, in order to bring our two year old Plymouth, I had to pay $900 in duty, which meant wiping out our meager savings. Three years later when we left Barranquilla, the car would be sold for less than the duty that was paid. I complained about this to the Department. Several officers were sympathetic with my complaint but offered no remedy. Barranquilla was the assignment. Take it or leave it. So, the thrill of entering the Foreign Service was marred a little bit. But it was further marred when I was told that taking one of the Grace Line boats that regularly stopped in Barranquilla was out of the question. First of all, the person I was replacing had already left the post, so I was needed urgently. Besides, the Department was stopping or trying to discourage travel by boat to cut down on per diem. So, we arrived in Barranquilla by plane in the first days of January 1952. I think it was about the third of January. These early disappointments made me wonder what I had gotten into and whether I should remain in the Foreign Service. The consulate in Barranquilla was a small post. It consisted of the Consul, Doug Flood, and two Vice Consuls. As the junior, I was the one responsible for issuing visitor and immigration visas, handling citizenship matters, protecting American citizens in trouble (such as American seamen who jumped ship, which was a fairly common occurrence) or dealing with Americans who were wanted for crimes in the United States who had fled to Colombia. This involved having to deal with the local police authorities. What also added to the consulate’s workload was Barranquilla’s geographical location. Under the 1952 McCarran Immigration Act, persons seeking to immigrate to the United States who had previously immigrated to countries contiguous to the United States were ineligible for immigration, much less for obtaining a visitor’s visa, unless they had resided at least two years in these contiguous countries. Well, contiguous territory was defined to include Canada, Mexico, islands in the Carribean, and the Central American republics, including Panama. So, Barranquilla, as the nearest non-contiguous Consulate, became a real 10
Description: