Albrecht effect aka the second aerosol indirect effect PDF
Preview Albrecht effect aka the second aerosol indirect effect
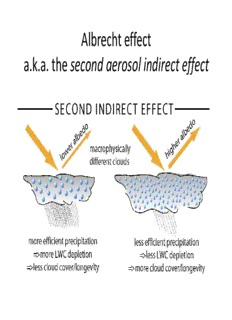
Albrecht effect a.k.a. the second aerosol indirect effect Differences in precipitation “efficiency” between continental and marine clouds Battan, L. J., and R. R. Braham, 1956: A Study of Convective Precipitation Based on Cloud and Radar Observations. J. Meteorol.,13, 587–91 Squires, P., 1958: The Microstructure and Colloidal Stability of Warm Clouds. Tellus, 10, 262–71. Hudson, J. G., 1983: Effects of CCN Concentrations on Stratus Clouds. J. Atmos. Sci., 40, 480–86. Hocking size limit Later calculations for collision efficiency of small drops • Sharp drop‐off in collision efficiency when small drop radius r < 8 m (the Hocking limit) A Short Course in Cloud Physics, Third Edition (International Series in Natural Philosophy), M K Yau, R R Rogers Albrecht “effect” • Mentions effect of drizzle on stabilizing PBL • Model: Albrecht trade‐Cu model, modified to include precip. Models cloud fractional cover using an RH‐based parameterization. Key processes controlling PBL clouds Radiative (left) and latent (right) heating rates Informed by aircraft observations From Brost, R. A., J. C. Wyngaard, and D. H. Lenschow, 1982: Marine Stratocumulus Layers. Part II: Turbulence Budgets. J. Atmos. Sci., 39, 818–36. Also…Nicholls, S., and J. Leighton., 1986: An Observational Study of the Structure of Stratiform Cloud Sheets: Part I. Structure. Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc., 112, 431–60.
Description: