Tracker July 2020 PDF
Preview Tracker July 2020
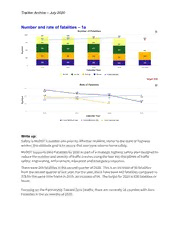
Tracker Archive – July 2020 Number and rate of fatalities – 1a Number of Fatalities 1000 !147 932 887 910 833 854 8•38 • - - 750 243 216 - 257 230 .; .0 E 500 442 z:J - - - - - 219 225 236 264 250 214 2016 2017 2018 2019 YTD 2020 Calendar Year e e e 4th Qlr JrdQtr 2nd Qtr 1s!Qtr -a-5-year average Target: 838 Rate of Fatalities 1.3 1.28 1.23 1.21 .; 12 1:.19 1.H 1 2 .0 E 1.17 1~8~ z:J 1.1 1.1 2016 2017 2018 2019 Calendar Year + 1-year Missouri rate + 5-year Missouri rate + 1-yearnational rate Write up: Safety is MoDOT’s number one priority. Whether resident, visitor to the state or highway worker, the ultimate goal is to assure that everyone returns home safely. MoDOT supports Zero Fatalities by 2030 as part of a strategic highway safety plan designed to reduce the number and severity of traffic crashes using the four key disciplines of traffic safety: engineering, enforcement, education and emergency response. There were 264 fatalities in the second quarter of 2020. This is an increase of 50 fatalities from the second quarter of last year. For the year, there have been 442 fatalities compared to 378 for the same time frame in 2019, an increase of 64. The target for 2020 is 836 fatalities or fewer. Focusing on the Partnership Toward Zero Deaths, there are currently 28 counties with Zero Fatalities in the six months of 2020. Tracker Archive – July 2020 Purpose: The fatal number measure tracks quarterly, annual and five-year average trends resulting from traffic crashes on all Missouri roadways. Measurement and Data Collection: Missouri law enforcement agencies submit a vehicle accident report form to the Missouri State Highway Patrol to be entered into a statewide traffic crash database. The database automatically updates MoDOT’s crash database system, which is part of the Transportation Management System. The rate of fatal crashes charts display annual and five-year average fatality and injury rates per 100 million vehicle miles traveled for these same crashes. In addition, the fatality rate chart includes the national average. Targets are based on Zero by 2030 fatality reduction, 1% VMT increase, and non-motorized reduction based on overall fatality and reductions. An exception is made for instances where the baseline five-year rolling average is less than the calculated target using the parameters previously described. When this occurs, the baseline will be used as the target. Number of fatalities in work zones – 1b Number of Fatalities in Work Zones 20 17 15 12 a:; 11 .E.0 10 - ii z::: ; 1 - 10 - 2016 (State) 2016 (local) 2017 (Stale) 2017 (local) 2018 (State) 2018 (local) 2019 (State) 2019 (local) YTD 2020 (State) YTD 2020 (local) Calendar Year 4th Qtr ■ 3rd Qtr ■ 2nd Qtr ■ 1st Qtr • 5-year average Target: Below 8 *2019 - Fatalities derived from TMS Tracker Archive – July 2020 Number of Crashes in Work Zones 2000 1,884 1,711 ii 1,503 1,543 •1,594 1500 •■ 395 336 1,•38 9 a:; .,. 296 _,,_ _,,_ .E.0 1000 ■ -'f- z:J 757 766 818 500 658 616497 ►1#93I N 175 189 335 _,,___ 451 178 -@i•- -ld2031 - lllii2&07 llil 280 NHN -.r10•r8- 1111 2016 (State) 2016 (Local) 2017 (State) 2017 (Local) 2018 (State) 2018 (Local) 2019 (State) 2019 (Local) YTD 2020 (Stale) YTD 2020 (Local) Calendar Year 4th Qtr ■ 3rd Qtr ■ 2nd Qtr ■ 1st Qtr + 5-year average Target: Below 1,389 *2020 - First quarter 2020 data is unavailable through the MSHP radio reports and is incomplete in TMS Write up: Safe, efficient travel for the public through work zones is important. All crews working in work zones are expected to conduct operations safely. MoDOT makes every effort to ensure this is the case and asks motorists to pay attention, slow down, move over, buckle up and drive without distractions. MoDOT’s goal is zero fatalities in work zones. Only through continued efforts from MoDOT, the contracting industry and the driving public can that goal be accomplished. There will be continual improvement in planning, available strategies and technologies employed. It is up to MoDOT to deploy the proper tools in each of the work zones. Based on information currently available, there have been seven fatal work zone crashes in calendar year 2020 on the state system and two fatal crashes on non-state system. The seven state system crashes all happened in the second quarter. Three of the crashes were rear-end collisions on the interstate where traffic was slowed in the work zone. One of those crash reports was not clear on the cause, one specifically mentioned that the driver was speeding and swerving immediately before the crash and the final one indicated that the driver was distracted and never applied their brakes. The nine fatal work zone crashes this year have resulted in a total of 11 fatalities. Of the eight people who were known or required to wear safety devices only three were wearing them. Poor driver behavior remains a primary factor in these fatal crashes which proves difficult for MoDOT to control. Community outreach and public awareness campaigns, such as Buckle Up Phone Down, are very helpful, but ultimately MoDOT is dependent upon the driving public to make good choices when driving in work zones. The challenges for MoDOT remain many, with changing driver behaviors at the top. Tracker Archive – July 2020 Purpose: This measure tracks the number of traffic-related and non-traffic-related fatalities, injuries and overall crashes occurring in work zones on state-owned and off-system roadways. Measurement and Data Collection: Missouri law enforcement agencies submit a vehicle accident report form to the Missouri State Highway Patrol to be entered into a statewide traffic crash database. The database automatically updates MoDOT’s crash database system, which is part of the Transportation Management System. MoDOT staff query and analyze this data to identify work zone related crash statistics. Missouri State Highway Patrol prioritizes entry of the crash reports by fatality, serious injury and property damage only. The target for this measure is updated quarterly. This target is established by projecting a 10% improvement over a five-year average. Number of vulnerable roadway user fatalities – 1c Number of Vulnerable Roadway User Fatalities 150 a; 100 .0 E z:J - 50 - - - 10 9 14 B 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Calendar Year e e e Motocycle Pedestrian Bicycle Desired Trend: Decrease Write up: In 2019 there was an increase in the number of vulnerable roadway users compared to 2018. Motorcycle fatalities increased 13%, pedestrian fatalities also increased 13%. Bicycle fatalities more than quadrupled in 2019 from 2018 and were one and a half times more than 2015-2017. Reviewing the fatalities for vulnerable users in 2019, five incidents involved drivers not following the rules of the road (failing to yield, speeding, using the wrong lane) and five where the cyclist didn't follow the rules of the road. In addition, two fatalities involved alcohol, one by the vehicle driver and one by the cyclist. The others were a suspected suicide and equipment malfunction. Developing strategies to focus on rules of the road for vehicle drivers and cyclists seems prudent. Tracker Archive – July 2020 The locations of the fatalities also provide focus areas: the Kansas City area had four fatalities, St. Louis had three and two were in the Springfield area. The worst months for fatalities were in June, July and August - each of which saw three fatalities. With higher fatalities during the summer months, releasing campaigns during those months is crucial. Purpose: The vulnerable roadway user measure tracks annual trends in fatalities of motorcyclists, pedestrians and bicyclists. These roadway users are at risk for death when involved in a motor-vehicle-related crash. Measurement and Data Collection: Missouri law enforcement agencies submit a vehicle accident report form to the Missouri State Highway Patrol to be entered into a statewide traffic crash database. The database automatically updates MoDOT’s crash database system, which is part of the Transportation Management System. Most common characteristics of fatal crashes – 1d Number of Fatalities 600 500 400 ;;; ..c E 300 z:J .. ., 200 = ·I.. li ! .., 1m 100 I ~ I " N I 0 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 Calendar Year e • Unrestrained Occupants • Run-Off-Road Aggressive Driving Alcohol and/or other Drugs • Curves • Intersection • Distracted Driving Write up: MoDOT’s priority is to keep customers and employees safe. The greatest challenge to this is the recurring frequency of fatal crashes and serious injury crashes on Missouri roadways. In order to combat this, MoDOT utilizes crash data to identify the most common contributing circumstances of severe crashes. By identifying behaviors and characteristics most associated with these crashes, MoDOT can make more informed decisions to address the problem. While the most common causes are related to human behavior, MoDOT can help implement solutions through education, enforcement, engineering and emergency response to minimize poor decisions and their potential impact. Missouri had 879 traffic fatalities in 2019. While nearly every category saw a decrease in 2019, aggressive driving continued to be the leading cause of fatal crashes in the state. Aggressive Tracker Archive – July 2020 driving includes speeding, driving too fast for conditions, following too close and improper passing. These behaviors, along with impairment and distraction, account for most fatal crashes in the state. When coupled with the decision to not buckle up, the results are even more deadly. On a positive note, seat belt use in Missouri reached an all-time high in 2019, and the number of unbuckled fatalities was down 13% for the year. That said, 64% of the vehicle occupants killed in 2019 were not wearing a seat belt. Distracted driving crashes were also down for the year, though it should be noted that this behavior is often difficult for officers to prove and reflect in the crash report. Both measures indicate positive progress in two of MoDOT's targeted behaviors, buckling up and putting the phone down. Through the Statewide Transportation Improvement Program, MoDOT continues to program millions of dollars in safety improvements each year, including curve improvements, high friction surface treatment, paved shoulders, rumble strips and intersection improvements such as J-Turns, turn lanes and pedestrian accommodations. These improvements are being identified through a data-driven, benefit-cost analysis to maximize the return on investment. On average, the state sees a six to one return on investment with these improvements. In addition, MoDOT continues to take advantage of federal safety funds for educational and enforcement programs to reduce poor driving behaviors. These programs allow other safety partners in the state to get involved in effort to move Missouri toward zero deaths. MoDOT will continue evaluating and implementing programs that successfully reach new audiences and prioritize a culture of highway safety in Missouri. Purpose: The measure tracks annual trends in motor-vehicle-related fatal resulting from the most common contributing factors or highway features. This data represents seven of the top focus areas presented in Missouri’s Blueprint to Save More Lives. Measurement and Data Collection: Missouri law enforcement agencies submit a vehicle accident report form to the Missouri State Highway Patrol to be entered into a statewide traffic crash database, which is part of the Transportation Management System. MoDOT staff query and analyze this data to determine the number of unrestrained occupants in crashes, how often aggressive driving, distracted driving, alcohol and other drugs contribute to crashes, and whether or not the vehicles ran off the road, the crash occurred in a curve or the crash occurred at an intersection. The Highway Patrol experiences a lag in data entry each year which prohibits MoDOT from using current complete crash data. This lag is being reduced through a combination of efforts involving not only manual data entry, but also an increased emphasis in electronic data entry. Tracker Archive – July 2020 Number and rate of fatalities involving commercial motor vehicles – 1e Number of Fatalities Involving Commercial Motor Vehicles 160 2.4 120 1.8 <ii .c E so z:::, 40 0.6 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 Calendar Year e Fatalities • Crash Rate Target: Below 128 Write up: Commercial Motor Vehicles play a vital role in the nation’s economy by transporting the products that are needed. By tracking the number of CMV involved fatalities, MoDOT can target educational and enforcement efforts, as well as improve safety features along Missouri roadways. MoDOT partners with the Missouri State Highway Patrol, St. Louis Metropolitan Police Department, Kansas City Police Department and St. Louis County Police Department to keep people safe while traveling in and around CMVs. While efforts from MoDOT and the partner agencies are effective in improving safety on roadways, Missouri has not experienced a significant decrease in the number and rate of fatalities involving CMVs. Between 2015 and 2019, fatalities involving a CMV increased by 19.2% and the fatality rate slightly increased from 1.22 to 1.24 per 100 million CMV vehicle miles traveled. In 2019, Missouri experienced a decrease of four fatalities involving a CMV as compared to 2018. This resulted in a 2019 fatality rate of 1.24 compared to 1.33 for 2018. Purpose: This measure tracks annual trends in fatalities involving Commercial Motor Vehicles. This data guides the development and focus of the Commercial Vehicle Safety Plan, which is the plan required to receive Motor Carrier Safety Assistance Program funds. Measurement and Data Collection: Missouri law enforcement agencies submit a vehicle accident report form to the Missouri State Highway Patrol to be entered into a statewide traffic crash database. The database automatically updates MoDOT’s crash database system, which is a part of the Transportation Management System. The fatal rates on the charts display the annual fatality and injury rates per 100 million vehicle miles traveled for commercial motor vehicles for these same crashes. The targets are based on a 9% improvement rate from the immediate prior year fatalities from the immediate prior year. Tracker Archive – July 2020 Percent of seat belt/passenger vehicle restraint use – 1f Percent of Seat Belt/Passenger Vehicle Restraint Use - 100 425 8•9.6 87.7 75 40 Cl C: c., j, C: ro <Oi i so 37 S mCl:'. c.. C: 0 z~ 25 35 32 S 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 Calendar Year e Nationwide Primary States e Missouri e Nationwide Secondary States + National Ranking (1st=Best) Write up: Seat belts save lives, but getting people to use them – even to protect their own lives – is a challenge. Public education is one way to keep the issue in front of motorists, along with legislation. MoDOT supports each approach, attacking the problem with focused marketing campaigns and reinforcing it with hard facts to back legislative efforts. Several municipalities across the state are taking matters into their own hands, enacting primary ordinances within city limits. Missouri currently has one county and 63 municipalities that have adopted primary seat belt ordinances, representing over 27% of the state’s population. Based on 119,413 observations, seat belt use in Missouri for 2019 was 87.7%, a 0.6% increase from 2018. Gasconade County was the lowest at 67.7% and Callaway County was the highest at 96.0% (weighted data). The national average for seat belt use in 2018 was 89.6% (2019 data is not yet available). Missouri’s national ranking (including Washington DC) in 2018 was 34th, with 17 states ranking lower in seat belt use. States with a primary seat belt law generally rank highest on seat belt use nationwide, while states that have a secondary law continue to rate lowest in national rankings. MoDOT is improving its safety culture through statewide strategic initiatives such as Buckle Up Phone Down and by coordinating Click It or Ticket, Youth Seat Belt and Child Passenger Safety Campaigns, as well as providing educational programs such as Teens Taking Action To Prevent Traffic Crashes and ThinkFirst. Purpose: This measure tracks annual trends in seat belt use in passenger vehicles. This data drives the development and focus of the Missouri Highway Safety Plan and supports Missouri’s Blueprint to Save More Lives. Tracker Archive – July 2020 Measurement and Data Collection: Each June, a statewide survey is conducted at 560 preselected locations in 28 counties. The data collected is calculated into a seat belt usage rate using a formula approved by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Data collection locations are selected from counties that represent 85 percent of the state’s vehicle occupant fatalities. While the data collection plan is the same each year for consistency, NHTSA guidelines require survey sites to be re-selected every five years based on updated fatality data. The 2018 survey is the first survey using updated survey sites since Missouri’s new survey methodology started in 2013. The target for this measure is updated annually in October for the next calendar year. This target is established as the current national average. Employee safety focus areas – 1g - Employee Safety Focus Area Backing 150 c.",' 100 I I I ·";C:; I .E 50 2016 2017 2018 2019 YTD 2020 Calendar Year • Incidents • Year to Date Employee Safety Focus Area - Slips, Trips and Falls 200 150 c"' ., I I ·";C:; 100 I I .E 50 ■ 2016 2017 2018 2019 YTD 2020 Calendar Year • Incidents • Year to Date Tracker Archive – July 2020 Employee Safety Focus Area Strains and Sprains 150 1":' 100 1. ·"u"C' I • ..5 50 2016 2017 2018 2019 YTD2020 Calendar Year • Incidents • Year to Date Write up: MoDOT’s number one value is safety. The purpose of this measure is for everyone to arrive at work safely and return home the same way. This includes all the preparation necessary for a safe day including planning the jobs, Risk Based Assessment review, morning safety briefings and stretching. This measure focuses on improving three high risk areas: backing a motorized vehicle; slips, trips and falls; and sprains and strains. MoDOT had 48 backing incidents in the first two quarters of 2020. While this is a 24% decrease from the same time frame in 2019, even one backing incident is too many. Backing incidents can cause property damage, injuries and death. Improvement strategies include parking to avoid backing, good planning, always using a spotter and doing a thorough circle check of the area. There were 59 employees who received medical attention for slips, trips and falls during the first two quarters of 2020, which is a 21% decrease from the same time frame in 2019. Improvement strategies include being aware of surroundings, keeping work areas organized, looking out for each other by pointing out hazards on the job that may be hidden. During the first two quarters 2020, 48 of MoDOT employees received medical attention for sprains and strains. This is a 2% increase from the same time frame in 2019. Improvement strategies include morning and afternoon stretching, asking for help when lifting and using proper lifting technique. It is imperative employees focus on improvement strategies and put MoDOT’s Behavior Based Safety and Actively Caring programs into action. At MoDOT, safety is everyone’s responsibility. Purpose: This measure tracks the department's most frequent incident types and highlights areas to focus on for improvement.
