Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia Study 2 PDF
Preview Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia Study 2
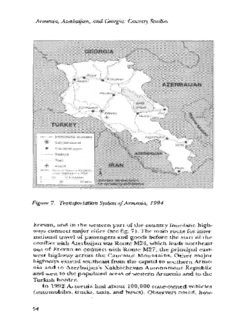
Armenia, Azerbajan, and Georgia: Country Studies N AZERBAIJAN •)L '" ,) SetIa1) Zod) t' A:kot - A rpo1 NOTE Slatus of agctrr1n.Karabakh under negohlafton Pr 994 A o 25 55 KIIopneIers o ,s 50 MIps not Figure 7. Transportation System of Armenia, 1994 Erevan, and in the western part of the country four-lane high- ways connect major cities (see fig. 7). The main route for inter- national travel of passengers and goods before the start of the conflict with Azerbaijan was Route M24, which leads northeast out of Erevan to connect with Route M27, the principal east- west highway across the Caucasus Mountains. Other major highways extend southeast from the capital to southern Arme- nia and to Azerbaijan's Nakhichevan Autonomous Republic and west to the populated areas of western Armenia and to the Turkish border. In 1992 Armenia had about 100,000 state-owned vehicles (automobiles, trucks, taxis, and buses). Observers noted, how- 54 Armenia ever, that at any given time about one-third of these vehicles were inoperable because of poor maintenance and unavailabil- ity of spare parts. Average vehicle age in 1992 was 6.5 years. Armenia had 825 kilometers of mainline railroad track in 1992, excluding several small industrial lines. Most lines are 1.520-meter broad gauge, and the principal routes are electri- fied. The rail system is roughly configured like a "Y" and has lines radiating from a central point just south of Erevan. The northeast branch roughly parallels Route M24 to Azerbaijan. About 85 percent of all goods used in Armenia are imported by rail, and before the conflict with Azerbaijan, most came via this rail line. Closure of the line at the international border during the early 1990s has caused severe disruption to the Armenian economy. The southern branch of the line extends south toward the Turkish border, where it turns southeast into Nakhichevan. The war with Azerbaijan has stopped service on this segment of the rail system as well. In 1994 the last operative portion of the country's rail lines UII was the northwest branch of the which winds through the populated areas of northwestern Armenia before crossing into Georgia. A short spur of this line at Gyumri connects with the Turkish rail system. However, a difference in gauge with the Turkish system means that goods crossing the Turkish border must undergo a time-consuming reloading process. In 1991 Armenia Railways, the state-owned rail system, oper- ated with 100 electric and eighty diesel locomotives. Delays in the delivery of spare parts from Russia have been a nagging problem in the maintenance of the system. Cannibalization of rolling stock to obtain parts has severely reduced service. Erevan's new subway system was still largely under construc- tion in the early 1990s. In 1994 nine stations had opened on the first ten-kilometer section of heavy-rail line. This first line connected Erevan's industrial area with the downtown area and the main rail station. Work on an additional four kilometers was slowed by the 1988 earthquake. Plans called for an eventual system of forty-seven kilometers organized into three lines. Armenia's principal airport, Zvartnots, is about seven kilo- meters from downtown Erevan. With a runway approximately 2,700 kilometers long, the airport can handle airplanes as large as the Russian Tu-154 and IL—86 or the Boeing 727. In 1993 the airport handled about 34,000 tons of freight. The State Airlines Company of Armenia, the new state-run airline, provides direct or nonstop service to about a dozen cities of the former Soviet 55 Armenia, Azerbayan, and Georgia: Country Studies Union, as well as to Paris. The Russian and Romanian national airlines also provide regular international air service into Ere- van. Since the beginning of the conflict with Azerbaijan, fuel shortages have curtailed expansion of passenger and cargo ser- vice, however. Several other airports elsewhere in Armenia have paved runways, but most are used for minor freight trans- port. Although air cargo has the potential to relieve the effects of the Azerbaijani blockade of land routes, efforts to fly in avia- tion kerosene were frustrated in 1993 by corruption in the Main Administration for Aviation and by high prices charged by Russian suppliers. Armenia's one major natural gas pipeline branches off the main Transcaucasian line that runs from Russia through Geor- gia to Baku. The Armenian spur begins in western Azerbaijan and reaches its main terminus in Erevan. In all, Armenia has 900 kilometers of natural gas pipeline. Armenia imports most of its fuel and, before the conflict with Azerbaijan, imported 80 percent of its fuel from Azerbaijan via the pipeline or in rail tanker cars. Like Armenia's rail and highway links, the pipeline from Azerbaijan has been closed by the Azerbaijani blockade. In 1991 the American Telephone and Telegraph Company installed 200 long-distance circuits in Armenia, which gave the republic the capacity, available elsewhere in the former Soviet Union only in Moscow, to receive direct-dial international calls. Radio and television are controlled by the State Committee for Television and Radio Broadcasting. Ten AM and three FM radio stations broadcast from Erevan, Kamo, and Sisian. Broad- casts are in Armenian, Kurdish, and Russian to points within Armenia, and in those languages plus Arabic, English, French, Persian, Spanish, and Turkish to points outside the country. The single television station broadcasts in Armenian and Rus- sian. According to Soviet statistics of the late 1980s, between 90 and 95 percent of Armenian homes had radios or televisions. No statistics are available for the blockade years, but experts believe that under blockade conditions substantially fewer Armenians have had regular access to broadcast information. Foreign Trade In the Soviet period, Armenia traded almost solely with the union's other republics. A foreign trade organization (FTO) controlled each product group, and exports by each Armenian enterprise were determined by the State Planning Committee (commonly known by its Russian acronym, Gosplan) in Mos- 56 Armenia cow. Enterprises had no control over the size or destination of shipments of their products. Together with Estonia and Tajiki- stan, Armenia had the highest level of imports among the Soviet republics. Its exports consisted mostly of semifinished goods that needed processing in other republics. In the years since the breakup of the Soviet Union, Arme- nia's economy has been hurt by the need to import much of its food and almost all of its oil and gas. In 1989 the FTO monop- oly was removed, allowing enterprises to seek their own buyers and sellers abroad. In 1992 the government removed most state controls over foreign trade. Export licensing continued to protect enterprises from fraud and to enforce domestic market quotas. In the early 1990s, most of Armenia's exports went to Russia, Eastern Europe, and various developing countries (see table 8, Appendix). ByJanuary 1992, Armenia had signed bilat- eral trade protocols with most of the former Soviet republics. To ensure flexibility in the face of future price liberalization, prices were to be set in direct negotiation between enterprises. Enterprises were not strictly bound by protocols signed by their respective governments, although quotas remained a possibil- ity. At this stage, all payments were to be in rubles. In 1990 Armenia's largest sources of export income were light industrial products (mostly knit clothing, shoes, and car- pets), machines and metal products, processed foods, and chemical products. The highest total expenditures on imports were for light industrial products, processed foods, chemical products, energy and fuels, and unprocessed agricultural prod- ucts. In 1990 Armenia showed a trade deficit of 869 million rubles in industrial goods and a deficit of 278 million rubles in agricultural goods. In April 1992, Armenia became the first former Soviet republic to sign a comprehensive bilateral trade agreement with the United States and the first to receive most-favored- nation status. Canada soon followed in granting Armenia simi- lar status. In planning future trade, Armenia expected to rely heavily on foreign markets for products from its newlyorga- nized complex of chemical enterprises, for which demand was identified in the former Soviet republics, Eastern Europe, Iran, Syria, Turkey, Argentina, and Australia. Government and Politics The Republic of Armenia declared its sovereignty on August 23, 1990, and became an independent state a year later, on Sep- 57 Armenia, Azerbazjan, and Georgia: Country Studies tember 23, 1991. In October 1991, Levon Ter-Petrosian, who had been elected democratically as chairman of the Armenian Supreme Soviet under the Soviet system in 1990, was chosen president of the republic in a six-candidate election. As of early 1994, Armenia was a reasonably stable democratic state, although its party structure was fractious and its legislative branch ineffectual. Because no consensus could be reached on a new constitution, a standoff between parliament and the president remained unresolved in early 1994. Parliament The 248 members of Armenia's unicameral parliament (Geraguin khorhurt in Armenian, officially retaining the term "Supreme Soviet" from the communist era) are elected for five- year terms and meet for six months each year. The prime min- ister and the Council of Ministers, which together constitute the executive branch of the government, are chosen from par- liament. Although hail the members of parliament (124) must be present for a quorum, a majority of the votes of the entire body (125) is needed to pass laws. In the early 1990s, because more than 160 members were rarely present and the ruling party did not have a majority in the body, the parliament was proving unable to act decisively on major legislative issues. Moreover, a two-thirds majority of the parliament (165) is needed to override a presidential veto. In the absence of a con- stitution, however, the parliament has issued laws regulating the relations and powers of the branches of government. The Presidium, the parliament's executive body, administers parliament when it is not in session. The Presidium is made up of the president of the republic (whose title is also chairman of parliament), two deputies, the secretary of the parliament, and the twelve chairmen of the permanent parliamentary commit- tees. Often laws are initiated by the president of the republic, sent to the Presidium for review, and then passed on to appro- priate committees before being reviewed and voted upon by the whole parliament. (Besides permanent committees, the parliament can create temporary committees to deal with spe- cific issues.) Once parliament passes a law, the president of the republic, who also may participate in parliamentary debates, must sign or veto within two weeks. In early 1994, parliamenthad not yet passed legislation replacing Soviet-era laws in several major areas: criminal and civil codes, administrative violations, mar- 58 Armenia riage and family, labor rights and practices, land tenure, and housing. The Presidency As it has developed in the 1990s, the Armenian presidency is the most powerful position in government. More than a cere- monial head of state, the president is the most active proposer of new legislation, the chief architect of foreign and military policy, and, during Armenia's prolonged state of national emergency, the unchallenged center of government power in many areas. Levon Ter-Petrosian, a former philologist and a founding member of the Karabakh Committee, became the first presi- dent of independent Armenia in 1991. Ter-Petrosian has occu- pied the political center of Armenian politics as the single most important politician in the country and the principal advocate of moderate policies in the face of nationalist emotionalism. The parliamentary plurality that Ter-Petrosian's party, the Armenian Pannational Movement (APM), enjoyed at the for- mation of the republic in 1991 enhanced presidential authority at the expense of parliament, where the majority of seats were divided among many parties. Beginning in 1992, Ter-Petrosian took several controversial unilateral actions on major issues, which brought accusations of abuse of power. State Administrative Bodies The Council of Ministers, which performs the everyday activities of the executive branch of government, is presided over by the prime minister, who reports directly to the presi- dent and to parliament. The prime minister is named by the president but must be approved by parliament. The members of the council are appointed by joint decision of the president and the prime minister. The Council of Ministers underwent a series of changes in the early 1990s as Ter-Petrosian sought a prime minister with whom he could work effectively. As a result, four men occupied that position between 1991 and 1993. The principal source of friction within government circles is factional disagreement about the appropriate elements and pace of economic reform. In the first years of independence, most of the members of the council have belonged to the APM. In 1994 the Council of Min- isters included the following ministries: agriculture, architec- ture and urban planning, communications, construction, 59 Armenia, Azerbajan, and Georgia: Country Studies culture, defense, economics, education, energy and fuel, envi- ronment, finance, food and state procurement, foreign affairs, health, higher education and science, industry, internal affairs, justice, labor and social security, light industry, national secu- rity, natural resources, trade, and transportation. In addition to the regular ministries, state ministries coordi- nate the activities of ministries having overlapping jurisdic- tions. State ministers rank higher than regular ministers. In 1994 there were six state ministries: agriculture, construction, energy and fuel, humanitarian assistance, military affairs, and science and culture. State agencies have responsibilities similar to those of ministries, but they are appointed by and report directly to the president. Seven state agencies were operating in 1994. The Judiciary With no constitution in place, the structure of the new Armenian judiciary remains unformalized. Most judges are holdovers from the Soviet period, and the power to appoint judges has not been decided between the legislative and execu- tive branches. Appointment and training of new judges are high priorities in replacing the Soviet judicial system with an independent judiciary. District courts are the courts of first instance. Their judges are named by the president and confirmed by the parliament. The Supreme Court, whose chief justice is nominated by the president and elected by a simple majority of parliament, pro- vides intermediate and final appellate review of cases. The court includes a three-member criminal chamber and a three- member civil chamber for intermediate review and an eleven- member presidium for final review. The full, thirty-two-mem- ber court provides plenary appellate review. The general prosecutor is nominated by the president and elected by parliament. The general prosecutor's office moves cases from lower to higher courts, oversees investigations, pros- ecutes federal cases, and has a broad mandate to monitor the activities of all state and legal entities and individual citizens. The general prosecutor appoints district attorneys, the chief legal officers at the district level. The Constitution Asof early 1994, adoption of a constitution for the Republic of Armenia remained a controversial and unresolved project. 60 Armenia In the meantime, the 1978 constitution, a replica of the Soviet Union's 1977 document, remained in effect except in cases where specific legislation superseded it. At the end of 1992, the president and the APM parliamentary delegates presented a draft constitution. They put forward a revised version in March 1993. Then, after nearly a year's work, a bloc of six opposition parties led by the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (ARF) presented an alternative constitution inJanuary 1994 that would expand the parliament's power, limit that of the presi- dent, expand the authority of local government, allow Arme- nians everywhere to participate in governing the republic, and seek international recognition of the 1915 massacre. As 1994 began, observers expected a long struggle before parliament adopted a final version. Local Government The republic is divided into thirty-seven districts, or gavar- ner, each of which has a legislative and administrative branch replicating the national structures. Pending adoption of a new constitution prescribing a division of power, however, all major decisions are made by the central government and are merely implemented by the district administrations. Political Parties During Armenia's seventy years as a Soviet republic, only one party, the Communist Party of Armenia (CPA), was allowed legal status. As a branch of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, it ruled under the direct orders of the leadership in Moscow. Following the collapse of communist authority, two major parties and dozens of minor ones competed for popular- ity along with the remnants of the CPA. In the years following independence, the most vocal and powerful opposition party was the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (ARF). Founded in 1890, the ARF was the ruling party in the Republic of Armenia in 1918—20; forbidden under the communist regimes, the ARF built a strong support net- work in the Armenian diaspora. When the party again became legal in 1991, its foreign supporters enabled it to gain influ- ence in Armenia out of proportion to its estimated member- ship of 40,000. With a platform calling for a coalition government, greater power for the parliament at the expense of the executive, and a strong social welfare program, the ARF gained eighteen seats in the 1992 parliamentary election. 61 Armenia, Azerbajan, and Georgia: Country Studies The Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), founded in 1921, calls for privatizing the economy and rapidly establishing all possi- ble conditions for a free-market economy. It also backs a strong system of state social welfare and recognition of Nagorno-Kara- bakh's independence. The LDP had seventeen seats in parlia- ment in 1994. Former dissident Pariur Hairikian heads the National Self-Determination Union, which has called for a coalition gov- ernment based on proportional representation of each party. With only one seat in parliament, the union takes a radical- right position on most issues. Extreme nationalist parties with racist ideologies also have small followings. Most opposition parties have been critical of Ter-Petrosians Nagorno-Karabakh policy; in 1992 they formed the so-called National Alliance to coordinate their foreign policy positions. Because of parlia- ments institutional weakness, oppositionists frequently have organized massive public rallies demanding the presidents res- ignation. In the first years of independence, the ruling elite came pri- marily from the Armenian Pannational Movement (APM), the umbrella organization that grew out of the Karabakh move- ment. In the 1992 parliamentary election, the APM gained fifty-five seats, easily giving it a plurality but leaving it vulnera- ble when opposition coalitions formed on individual issues. The next largest delegation, that of the ARF, had twelve seats. In 1993 the failure of Ter-Petrosian's government to bring the Karabakh conflict to an end, its own willingness to compromise on the Karabakh question, and the daily grind of fuel and food shortages reduced the popularity of the ruling nationalist movement. Human Rights In April 1991, Armenia signed the International Covenant of Civil and Political Rights and accepted it as domestic law, superseding all existing laws on the subject. That covenant includes the right to counsel; the presumption of innocence of the accused; the right to privacy; prohibition of arbitrary arrest; freedom of the press, religion, political expression and assem- bly, and movement; minority rights; and prohibition of discrim- ination. Since 1991 specific legislation has further guaranteed freedom of the press and prohibited discrimination in educa- tion, language, and employment. Rights of the accused, how- 62 Armenia ever, remain undefined pending Armenia's acceptance of international conventions on that subject. In 1993 several human rights organizations were active in Armenia: the Helsinki Assembly, which represented the inter- national Helsinki Watch; the League of Human Rights; parlia- ment's Committee on Human Rights; a national group called Avangard; and a branch of the international Sakharov Fund. In 1993 the National Self-Determination Union accused the Ter-Petrosian government of a state terrorism policy that included the assassination of individuals within the union and others opposed to government policy. The most publicized incident was the murder in 1993 of Marius Yuzbashian, a former chief of the Armenian branch of the Committee for State Security (Komitet gosudarstvennoi bezopasnosti—KGB). The Media In the Soviet era, the officially sanctioned source of public information was Armenpress, the state news agency assigned to disseminate the propaganda of the CPA. In the post-Soviet years, Armenpress has remained the primary source of infor- mation for independent newspapers in Armenia and for peri- odicals in the diaspora. Under those conditions, the agency has required continued state funding to maintain its information flow to foreign customers, of whom seventeen had reciprocal information supply agreements with Armenpress in early 1994. Meanwhile, the agency has adopted a more neutral position in its reporting. Early in 1994, the Ministry of Justice reported that twenty- four magazines, nine radio stations, twenty-five press agencies, and 232 newspapers were active. Several national newspapers represent a variety of political viewpoints. Hayastani Hanrapetu- tiun (Republic of Armenia) is the official daily newspaper of the Supreme Soviet, published in Armenian and Russian ver- sions. GobsArmenii (The Voice of Armenia), published daily in Russian, is the official organ of the CPA. Azatamart (Struggle for Freedom) and Hazatamart (Battle for Freedom) are weekly organs of the ARF. Hazg (Nation) is published by the Party of Democratic Freedom. Other newspapers include Grakan Tert (Literary Paper), published by the Armenian Union of Writers; Hayk (Armenia), a publication of the APM; Ria Taze (New Way); and Yerokoian Yerevan (Evening Erevan). In 1993 thirteen major magazines and journals covered science and technology, politics, art, culture, and economics; the group also included 63
Description: