A FLORISTIC SURVEY OF NATIONAL PARK SERVICE AREAS OF TIMUCUAN ECOLOGICAL AND HISTORIC PRESERVE (INCLUDING FORT CAROLINE NATIONAL MEMORIAL), DUVAL COUNTY, FLORIDA PDF
Preview A FLORISTIC SURVEY OF NATIONAL PARK SERVICE AREAS OF TIMUCUAN ECOLOGICAL AND HISTORIC PRESERVE (INCLUDING FORT CAROLINE NATIONAL MEMORIAL), DUVAL COUNTY, FLORIDA
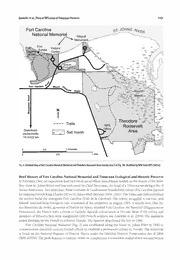
A SURVEY OF NATIONAL PARK AREAS OE TIMUCUAN FLORISTIC SERVICE AND ECOLOGICAL HISTORIC PRESERVE (INCLUDING EORT CAROLINE NATIONAL MEMORIAL), DUVAL COUNTY, FLORIDA Wendy Zomlefer David Giannasi B. E. Department Department of Plant Biology of Plant Biology University of Georgia la 2502 2502 Plant Sciences Plant Sciences Athens, Georgia 30602-7271, Athens, Georgia 30602-7271, U.S.A. U.S.A. SJudd Walter Department of Botany University of Florida Box 8526 P.O. 11 Gainesville, Florida 3261 1-8526, U.S.A. ABSTRACT The portion of the Timucuan Ecological and Historic Preserve (including Fort Caroline National Memorial) administered by the National Park Service, U.S. Department of the Interior, comprises 3,723 ha (9,200 acres ina series of disjointed land parcels in eastern Jackson- ) A ville, Duval County, Florida. floristic survey was conducted to provide Park Service personnel with a vouchered checklist of vascular plant species, supplemented with salient information such as relative abundance, locality data, and community type. Three intensive collecting trips conducted in 2005 yielded 480 taxa (474 species plus 6 varieties) of vascular plants in 318 genera of 122 families. The A five largest families are Asteraceae, Poaceae, Cyperaceae, Fabaceae, and Ericaceae. map, descriptions, and photographs of the various plant communities are also provided. RESUMEN La porcion de la Reserva Ecologica e Biistorica de Timucuan, administrada por el Servicio de Parques Nacionales del Departamento del Interior, comprende 3,723 ha (9,200 acres) enungrupo de parcelas aisladas al este de Jacksonville, condado Duval, Florida. Se desarrollo un analisis florlstico con el objetivo de proveer al personal del Servicio de Parques Nacionales, de una lista de las especies de plantas vasculares, suplementada con informacion sobre abundancia relativa, localidad y el tipo de comunidad circundante. Se realizaron tres giras de recoleccion intensiva durante 2005, produciendo un total de 480 taxa (474 especies y 6 variedades) de plantas vasculares, de 318 generos y 122 familias. Las cinco familias mas representadas son: Asteraceae, Poaceae, Cyperaceae, Fabaceae y Ericaceae. De igual forma se aportan mapas, descripciones y fotografias de las diferentes comunidades vegetales. INTRODUCTION Study Area The Timucuan Ecological and Historic Preserve located within the city limits ofJacksonville, Duval County is Florida (Fig. lA), and is the largest cooperative park system in the United States, comprising federal, state, and city park lands, plus properties of private corporations, authorities, and over 300 private landowners NFS (Anderson et al. 1996; Furbish et al. 1996; 2007a). The large area, 46,000 acres (18,620 ha), encom- passes the St. Johns River valley between the lower St. Johns and Nassau Rivers (Fig. IB). These two rivers discharge directly into the Atlantic Ocean and form an extensive estuarine system dominated by marsh salt hammock and coastal habitat with marine brackish open waters. The preserve over 75 percent to itself is wetlands and open water (see Fig. IB). Dense housing developments (and other scattered pockets of urban growth) within preserve boundaries were established prior to formal land use planning for the area. Preserve upland areas are highly desirable for development due to their aesthetic value and proximity to open water. Industries, such as plant nurseries and construction companies, are concentrated west of the preserve, and rural residential development spread is out in lower density subdivisions in outlying tracts. Fstuarine wetlands and waters within the preserve are claimed under sovereignty of the state of Florida up to the mean tide line, and the city of Jacksonville has - J. Bot. Res. Inst. Texas 1(2): 1157 1178.2007 1158 Journal of the Botanical Research Institute of Texas 1(2) 83° 82° 81° 1 Fernandina Beach Ocean Atlantic Jacksonville Beach o 30 Augustine St. o 82° 83° 81 marsh ' salt Downtown Jacksonville Map Fig. 1. Location and boundaries of Timucuan Ecological and Historic Preserve. A. of northeastern Florida, showing location of Timucuan Preserve (Fig. 1B) with dark gray shading. B. Map of eastern Jacksonville, Duval County, showing preservearea (shaded), bounded by St. Johnsand Nassau Rivers. Park area includes waterways between the extensive salt marsh areas; the northern boundary (not shown) bisects the Nassau River along its length. = = Darker gray areas within the preserve =five survey parcels (NPS land): 1=ThomasCreek;2 Cedar Point; 3 Fort Caroline National Memorial/Theodore = = = = Roosevelt Area (see Fig. 2); 4 Kingsley Plantation; 5 Sohn Purchase. BHI Black Hammock Island; PR private property inholdings. A: modified WBZ WBZ by from DeLorme (1 997); B: modified by from Furbish et al. (1 996) and NPS (2004, 2005, 2007a). Zomlefer et Flora of NPS areas of Timucuan Preserve 1159 al.. jurisdiction over zoning and land use. The various administrative agencies and private citizens work through common cooperative partnerships toward acquisition and management goals (Anderson 1996). et al. The areas within the preserve controlled by the National Park Service (NPS; U.S. Department of the NPS Interior), comprise ca. 9,200 acres (3,723 ha; 2004) of disjointed land parcels, including Fort Caroline NPS National Memorial, discussed below (NPS 2007a). Over 60 percent of this acreage is salt marsh (and maximum submerged lands) bordering brackish waters. To obtain plant diversity over such a broad area NPS within three intense sampling the survey team focused on land parcels (dark gray areas labeled trips, five — ai "5" Thomas 1"^^ to in Fig. IB) Creek, Cedar Point, Fort Caroline National Memorial/Theodore Roosevelt — Area, Kingsley Plantation, and Sohn Purchase that encompass a wide range of habitat types (including on summarized disturbed areas). Descriptive data these habitats (discussed briefly below) are in Table I. — Thomas km) 1. Creek Parcel, ^This site, bordered along the east by 1-95, is located ca. 3 miles (5 northeast of the Jacksonville International Airport. The gated property accessed by easement through land is owned by Castleton Beverage Corporation subsidiary of the Bacardi Corporation) the end of Butch Bane (a at Thomas Drive East. To the northeast, the Nassau River splits into Creek, and a smaller tributary, Seaton Creek, swamp runs through the land more or less parallel to the interstate. Habitats comprise hardwood surrounded by pinelands that have been extensively logged; other disturbed areas include a water-filled borrow pit and who dike system (from interstate construction). Trespassing poachers, access the remote property along the NPS problem As easement interstate border, are a for personnel. of this writing, the future of the property, now A War may unknown. Revolutionary have been fought within property boundaries: for sale, is battle the Battle of Thomas Creek (17 May 1777), the final engagement in the second attempt by American forces to invade the British province of East Florida (Boatner 1973). However, the exact location of the battle has not been verified (R. Bryant, pers. comm.). — New 2. Cedar Point, Cedar Point is at the end of south Cedar Point Road (ca. 5 mi [8 km] east of hammock Berlin Road) and comprises extensive marsh surrounded by upland maritime and some salt Ham- former pine plantations. This property (and the Sohn Purchase, below) on the popular Black 5. is mock Island in northeastern Jacksonville, which bordered by the Nassau River to the north and extensive is marshes of the Johns River, to the south. (Cedar Point occupies the southwestern tip with wetlands of St. Hammock the Johns and George Rivers.) Black Island was only sparsely populated until the 1980 St. Ft. s when infrastructure for development (paved roads, mail delivery, garbage service) became widely available; Dames the opening of the Point Bridge (over the Johns River) in 1989 further stimulated the population St. now known boom. The general area is well for panoramic views of marshlands and waterways. Cedar Point is a former fish camp (with cleared areas for parking and a boat ramp). Plans by NPS to construct a visitors' may center there (with extensive hiking be delayed due recent archeological evidence indicating trails) to some comm.). historical significance to this site (R. Bryant, pers. — Fort Caroline National Memorial/Theodore Roosevelt Area. This property comprises the Fort 3. NPS Caroline National Memorial/Ribault Monument, headquarters/museum, and the Theodore Roosevelt Area (see detailed map. Fig. These combined areas, a significant inholding among very expensive homes 2). and riverfront property, have over 4 mi km] of publicly accessible through extensive hammock, [6.4 trails swamp, and salt marsh. Fort Caroline National Memorial (138 acres [56 ha]; including the fort exhibit, visitors' center, park maintenance buildings, parking area, and boat dock) located on the north side of is Monument Fort Caroline Road (just north of the intersection with Road) and borders the southern shore Monument mi km) of the St. Johns River; Ribault is in a small disjunct area (8 acres [3 ha]) about 0.7 (1.1 monuments further east along the river (see Brief History of these below.) Park headquarters located is Mount about mile the south along Pleasant Road, adjacent the Theodore Roosevelt Area the north a to to to and east. The latter ca. 578 acres (234 ha) of ecologically significant, valuable real estate were bequeathed to the Nature Conservancy by this property's last private owner, Willie Browne (1889-1970), in tribute to NPS President Theodore Roosevelt and his conservation The acquired the land in 1990. efforts. — NPS 4. Kingsley Plantation. The plantation (including offices and parking areas) is located on the northern point of Fort George Island, along the Fort George River. Most of the surrounding habitat (primarily 1160 Journal of the Botanical Research Institute of Texas 1(2) Table .Year of acquisition, size, location, significance, access, and liabitats of tlie five survey sites ofTimucuan Ecological and 1 Historic Preserve administered by the National Park Service, Jacksonville, Florida (Fig. 1 B). Data from Anderson et al. (1 996), = Bennett 976), NPS (2004), NP5 (2007a), and Bryant (pers. comm.). Habitat types: aq aquatic habitat (standing freshwater R. (1 and surrounding margin); da = disturbed area; du = dunes/open beach; mh = maritime hammock; pf = pine flatwoods; sa = = = = sandhill/scrub community; sh shell midden; sm salt marsh; sw swamp. Parcel Area Location Historical and/or Ecological Public Habitat [Year Acquired by NPS] ha (acres) Importance Access Types w I.Thomas Creek [1995] 243 (600) Dead end Butch Various wetland communities; No AQ, DA, PF, Bane gated possible of Revolutionary SW Dr. East, site entrance through War of Thomas Creek" "Battle easement property; Thomas bordered by Creek and 1-95 Hammock 2. Cedar Point [1996] 62 (400) Black Riverfront property, encroaching Yes DA, MH, SM 1 9023 Cedar development; Island: significant habitats PointRd.;nofSt. including extensive salt Johns and George marsh; possible archeologica Ft. Rivers significance 3. Fort Caroline National 293 (724) 12713 Fort Caroline Valuable real estate, encroaching Yes AQ, DA, DU, & Memorial Rd./13165Mt. development; memorial [1950] Ribault national H, SA, SH, Monument [1958 at its Pleasant Rd. (park sites; significant habitats SM, SW present location]/Theodore headquarters; including wetlands w Roosevelt Area Roosevelt Area of [1990] headquarters and sof see 2 fort); Fig. Nw 4. Kingsley Plantation 991 32 (80) Ft. George Island; Valuable real estate; early 19th Yes DA, DU, MH, [1 ] along George River century plantation, including SM Ft. planter's residence, slave quarters 5. Sohn Purchase [2001] 85(211) Black Hammock Island: Valuable real estate, encroaching No AQ, DA, SA, w gated entrance of development; significant habitats sw Saw 13501 including wetlands Pit Rd.; w of Nassau of s River, Pumpkin Creek hammock) disturbed. During Florida's plantation period (1763-1865), the isolated Fort George Island is was owned by a series of planters, including Zephaniah Kingsley and his wife, Anna (a former slave from who Senegal), lived there from 1814 to 1837 (Schafer 1997; Stowell and Tilford 1998; Mallard 2007). The primary cash crop was sea island cotton (Gossypium harhadense)^ grown for the exceptionally long fibers spun compound into fine strong thread. The existing comprises the restored planter's residence (ca. 1798) with heritage gardens, as well as the nearby ruins of the slaves' quarters (arranged in semicircle), constructed of One tabby (a mixture of oyster shells, sand, and water). cabin has been restored to its original appearance for the interpretive display. — 5. Sohn Purchase, The gated property, named after last private owner, located along the west its is side Saw Pit Road, ca. 1.5 mi (2.4 km) north of Cedar Point Road (see 2. Cedar Point above) and is in west- Hammock NPS central Black Island, a rural portion undergoing development. The area was acquired by in 2001 (R. Bryant, pers. comm.). The land is bordered to the west by Pumpkin Hill Creek, a southern branch swamp of Nassau River, which feeds the and wetlands (marsh and open water areas) of the northern, western, and southern parts of the property. Scrubby sandhill (last burned in 1993), densely covering the eastern and central portions, intergrades with the various wetland habitats. The extreme southern end of the property was burned in 1998. Zomlefer et Flora of NPS areas of Timucuan Preserve 1161 al.. ^OWA/S Fort Caroline ST. /?/t/^^ Memorial National Ribault Monument Fort r-. u.. tiifr ^- Visitors' Exhibit ALYPSO .1 1 j< Center ,\\\>, ,ihi. ISLAND .Ur ll' \'. .ill. .i r; / til J. .\\U \\u .1^ Spanish b LLlI Fh Pond V> + ri ri \\\ Ur — '^ b h P Hf M\i h- A^lr .1 Mr. ^Ui« \\i. u. ^1 1 Id l1 Jr I ll lplr.# ^\ \\t \l IH P .Hi^ i II M\i. ^ h |PjJ F O \\\. \ iili^ ill Fort Caroline Mount . L I P F ah - ^^^t Road 4^Round^ L .lI \. .i:j^ / y\\U ,ti Marsh •o .L Jl, .h I >^ 1 I* (D ^\\i^ O \i. cc A M. f. ^\\\\U b I\ 4uP.H .\\\i tl .\\U a[ ^rf c .\\ .1 I F. an. ,1 \{~ a> M\>. .\ £ ih'. 3 N C All/^/ ^\\\\l. o S .iH.. .. .till. ,\ r. I ^ F r ' ,if a Ji' M |p \. slUx, Theodore xllJl a h' >l I'. Trails NPS Roosevelt Downtown Area marsh Salt Jacksonville iL Ik. Ir \ t km 14 mi/22 aUi, 6 .\\U// .<::i Kilometer 1 Mile 1 map WBZ Fig. 2. Detailed of Fort Caroline National Memorial and Theodore Roosevelt Area (survey area 3 in Fig. 1 B). Modified by from NPS (2007a). Memorial and Timucuan and Brief History of Fort Caroline National Ecological Historic Preserve In February 1562, an expedition lead by French naval officer Jean Ribault landed on the mouth of the River May (now Johns River) and was welcomed by Chief Saturiwas, the head of a Timucua-speaking tribe of St. Native Americans. Two years Rene Goulaine de Laudonniere founded the colony of Caroline (named later, la for reigning French King Charles IX) on Johns Bluff (Bennett 1976, 2001). The Timucuan Indians helped St. the settlers build the triangular Fort Caroline (Fort de la Caroline). The colony struggled to survive, and command A month Don Ribault returned from Europe take of the settlement in August 1565. Pe- to later, dro Menendez de Aviles, governor of Florida for Spain, attacked Fort Caroline. As "heretics" (Huguenots or Protestants), the French were a threat to Catholic Spanish colonization in Florida. Most of the colony and members of Ribault's fleet were slaughtered (245 French soldiers; see Zomlefer et al. 2004). The massacre ended attempts by the French to colonize Florida. The Spanish abandoned the fort in 1569. Fort Caroline National Memorial was established along the lower Johns River in 1950 (Fig. 2) to St. commemorate sixteenth century French efforts to establish a permanent colony in Florida. The memorial listed on the National Register of Historic Places under the National Historic Preservation Act of 1966 is (NPS 2007b). The park features a visitors' center to complement a somewhat scaled-down reconstruction 1162 Journal of the Botanical Research Institute of Texas 1(2) of the fort (ca. 200 x 200 x 300 [61 x 61 x 91 m]) based on a sketch by Jacques le Moyne, the colony's ft mapmaker. Ribauk Monument, an obeUsk situated atop Johns Bluff, commemorates Jean Ribault's land- St. mouth The unknown ing near the of the St. Johns River. exact site of Fort Caroline (and the settlement) is when and was likely destroyed the river channel was deepened and widened in the 1880's (Anderson et al. NFS 1996; 2007a). Fort Caroline National Memorial specifically designated as a unit within the Timucuan Ecological is Law and Historic Preserve, authorized by Congress in 1988 through Public 100-249 (Furbish 1996). et al. The was and and which preserve created to protect interpret the ecological historical resources of the area, name include one of the few remaining unspoiled coastal wetlands along the Atlantic. The honors the ex- American Timucua who made with European tirpated native tribes, contact the arrivals to the area: first who "Timucua" actually refers to several culturally diverse tribes, sharing the same language, inhabited northern Florida and southeastern Georgia (Hann 1996). European diseases devastated the population, known and by 1700, less than 550 of these native Americans survived; today, no indigenous people are Timucua. AND METHODS MATERIALS The first authors, Zomlefer and Giannasi, led three intensive field trips in 2005 (21-24 April, 28 June-1 & July, 29 September-2 October; Giannasi Zomlefer 1184-1573, 1576-1738) to collect vascular plant speci- men vouchers in duplicate using standard and herbarium techniques (under NPS collecting permit # field TIMU-2003-SCI-OOOl) with assistance of coauthor Judd and personnel listed in the acknowledgments. Plant NPS associations were also assessed. The survey focused on five main land parcels administered by (Fig. IB; Table The floras of Wunderlin and Hansen (2000, 2003) were primary sources for plant identification, 1). supplemented by Godfrey and Wooten (1979, 1981) and Godfrey (1988). The majority of plants were identi- WBZ fied by and DEC; Stephen Lee Echols identified most grasses and sedges; and coauthor WSJ confirmed A A other problematic determinations. complete of vouchers deposited GA. duplicate the set is at set is at Museum NPS Timucuan and Ecological Historical Preserve (see 2007a); that collection hereafter designated is & "TIMU," Park Service acronym not registered in Index Herbariorum (Holmgren Holmgren 2007). a AND RESULTS DISCUSSION Floristics The 554 numbered collections comprise 480 taxa (474 species plus 6 varieties) in four major vascular plant ANNOTATED CHECKLIST OF groups (see SPECIES below): lycophytes monilophytes ("ferns and (1 sp.), gymnosperms allies;" 10 spp.), (7 spp.), and angiosperms (256 spp. + 6 vars.). Included in the list are 26 species planted around park headquarter/visitor buildings (Fort Caroline National Memorial, Theodore Roosevelt Area, and George Island; indicated as "cult"). The largest families are: Asteraceae (62 spp. + St. 1 var.), Poaceae (40 spp. + 3 vars.), Cyperaceae (26 spp.), Fabaceae (21 spp. + 1 var.), Ericaceae (16 spp.), Euphorbiaceae Rubiaceae Fagaceae Hypericaceae Juncaceae (11 spp.), (11 spp.), (10 spp.), (10 spp.), (10 spp.), Onagraceae (10 spp.), Lamiaceae (9 spp.), and Plantaginaceae (9 spp.). With completion of this survey, we new have vouchered 56 county records (54 species and two varieties) for Duval County, Florida, according Wunderlin and Hansen to (2007). & No state/federally listed endangered plants (Duever 1996; Coile Garland 2003; U.S. Fish and Wild- life Service 2007) and no Florida endemics were found; however, Liatris tenuijolia var. quadrijlora, cited in Wunderlin and Hansen (2003) as endemic to Florida, has been recently vouchered from Cumberland Island, Georgia (Zomlefer et al., in prep.). Three state listed threatened species were found: Drosera intermedia (water sundew), Opuntia stricta (erect pricklypear), and Sarracenia minor (hooded pitcherplant); in addition, Os- munda cinnamomea (cinnamon Osmunda and Rhododendron fern), regalis var. spectahilis (royal fern), canescens & (mountain commercially Garland azalea) are state listed exploited plants (Coile 2003). Excluding the 21 cultivated exotics, the remaining 61 introduced species represent 13.5% of the total. Eleven species (including three cultivated plants) are listed as invasive exotics by Florida Exotic Pest Plant Zomlefer et Flora of NPS areas of Timucuan Preserve 1163 al.. Council (FLEPPC 2007). Nine of these are ranked as Category (invasive exotics altering native plant com- I munities by displacing native species, changing community structures/ecological functions, or hybridizing Cinnamomum with natives): Asparagus aethiopicus, camphora, Dioscorea hulbijera, Eichhornia crassipes, Lantana Two camara, Lonicera japonica, Lygodiumjaponicum, Macjadyena unguis-cati, and Sapium sehiferum. species, Alternanthera philoxcroides and Wisteria sinensis, are in Category (invasive exotics increasing in abundance/ II frequency but not yet altered Florida plant communities to the extent shown by Category plants). Aspara- I gus aethiopicus (Sprenger's asparagus-fern) and Lonicera japonica (Japanese honeysuckle) are planted at the NPS Park offices (Kingsley Plantation, Ft. George Island) and apparently are restricted to their flower bed plots; however, at the same site Wisteria sinensis (Chinese wisteria) and Macjadyena unguis-cati (catclawvine) are naturalized and spreading. Lantana camara (lantana), represented by a few plants cultivated with L. depressa and L. montevidensis near a boat dock (just east of reconstructed Fort Caroline), has some potential to spread into the disturbed areas surrounding the fort. Lygodium japonicum (Japanese climbing fern) is lo- common hammock cally along the path through the maritime surrounding the fort and should be removed (common before invading further. Dioscorea hulhijera (air-potato) and Eichhornia crassipes water-hyacinth), common serious invasives, are and well established around Spanish Pond. The Thomas Creek Parcel has three invasive species in aquatic habitats where propagules are likely dispersed by water runoff from 1-95: Cinnamomum Alternanthera philoxeroides (alligatorweed; infrequent; dike area), camphora (camphortree; infrequent; swamp), and Sapium sehiferum (popcorntree; locally common; dike area and swamp). Of these, common many Sapium sehiferum the most in this land parcel: the seedlings, established along the margins is of these aquatic habitats and in standing water, have potential to rapidly displace native species, especially hardwood swamp. in the A significant native species in danger of extinction in the preserve due to a recent invasion of an is exotic insect. In late June 2005 coauthors Zomlefer and Giannasi noted dying redbay trees (Persea horhonia), likely infected with redbay wilt, in the maritime forests of Cedar Point after park service personnel had reported similar occurrences at Kingsley Plantation. The presence of this fungal disease carrier, redbay & ambrosia beetle (Xylehorus glabratus), was confirmed at the preserve in October of that year (Mayfield Thomas 2006). Redbay wilt has since spread widely along the coast (R. Bryant, pers. comm.; Zomlefer etal., in prep.). Persea horhonia a dominant understory component, and large-scale redbay mortality will greatly is alter the composition of maritime forests along these coastlines. Communities Plant Nine community types of the survey area are summarized below and several are depicted in Figure dune; 3: hammock; salt marsh; shell midden; maritime sandhill community; aquatic habitat (standing freshwater and surrounding margin); swamp; pine flatwoods; and disturbed areas. Table includes a listing of habitat types 1 in each of the five survey sites. Habitats often intergrade within a site. These general categories are based Monk upon our field observations and classifications of similar areas by Laessle and (1961), Stalter and Dial FNAI Myers and Ewel Fasley and Judd and Zomlefer (1984), (1990), (1990), (1993), et al. (2004). — Dunes/Open Beach, The open beach comprises exposed sandy beach up high and to the tide line, foredune is the zone bordering the open beach, often sparsely vegetated with salt tolerant, pioneer species & (Johnson Barbour 1990; Zomlefer 2004). Limited beach-like plant communities occur on narrow et al. sandy strips 15 m] wide) along the river beaches on the northern sides of Kingsley Plantation (ca. ft [4.6 (St. George River) and the Fort Caroline exhibit (St. Johns River). Typical beach species found at these locations include: Batis maritima^ Borrichiafrutescens, Cenchrus spinifex^ Hydrocotyle honariensis, Ipomoea alba, Oenothera and laciniata, Physalis walteri, Sarcoconia perennis, Sesuvium portulacastrum, Strophostyles helvola. — Marsh, marshes communities occupying Salt Salt in Florida are coastal of salt-tolerant plants intertidal zones at least occasionally inundated with salt water, characterized by dense stands o^ Spartina alterniflora & & (saltmarsh cordgrass) and/or Juncus roemerianus (black rush; Montague Wiegert 1990; Fasley Judd 1993; Zomlefer et 2004). Fxtensive expanses of salt marsh comprise Cedar Point, as well as the north- al. eastern portion of the Theodore Roosevelt Area (Round Marsh, Fig. 3D); smaller areas are located along the western side of Fort Caroline (Calypso Island) and western edge of Kingsley Plantation (Steinway-Rodkin 1164 Journal of the Botanical Research Institute of Texas 1(2) — 3. Examples of plant communities of Timucuan Ecological and Historic Preserve. A. Scrubby sandhill (Sohn Property, Sep 2005) dense overstory: Fig. mth Quercus geminata Hexvomitoria, Lyonia lucida, and Serenoarepens. B. Longleaf pine-turkey oak sandhill (NPS headquartersjheodore Roosevelt Zomlefer et Flora of NPS areas of Timucuan Preserve 1165 al.. & common Montague 2003). Besides saltmarsh cordgrass and black rush, salt-tolerant plants within these marshes include: Atriplex cristata, Balis maritima, Chenopodium album, Cynanchum angustijolium Distichlis , Limonium carolinianum, Sarcocorniaperennis, Sesuvium portulacastrum, and Suaeda These spicata, linearis. salt woody marshes bordered by such are plants as: Baccharis halimijolia, Borrichia Jrutescens, Ilex vomitoria, Iva Jrutescensjuniperus virginiana, Lycium carolinianum, Myrica cerijera^ Opuntia stricta, and Sahal palmetto. — Shell Midden (Shell Mound). This coastal habitat formed from the activities of native Americans is who created elevated mounds of mollusk shell fragments that become mixed with organic matter over time (Fig. 3F). Water drains rapidly through the calcareous substrate and supports a distinctive set of indicator species; a closed hardwood canopy eventually develops (FNAI 1990). Well-developed shell midden habitat occurs around the salt marshes of the Theodore Roosevelt Area (Round Marsh, Fig. 3E), mainly as a sparse shrubby community intergrading with maritime hammock. The scrubby overstory species include: Forestiera segregata, Ilex vomitoria, IvaJruteseens.Juniperus virginiana, Myrica cerifera, Quercus geminata, and Sahal pal- — metto with tangled vines oi Cynanchum scoparium and Smilax auriculata. Borrichiajrutescens, Chiococca alha, common Eustachys petraea, Iresine rhizomatosa, Opuntia pusilla, and Psychotria nervosa are in the understory. — Hammock Hammodz; Maritime Maritime (Coastal Forest), ^This habitat, the terminal stage of suc- cession in coastal areas, is a band of "hardwood" forest just inland of the coastal strand on old, stabilized & Monk dunes; the generally mesic conditions are maintained by the dense canopy (Laessle 1961; Stalter & & hammock Dial 1984; Fasley Judd 1993; Zomlefer 2004). Well established maritime borders the et al. salt marshes of Fort Caroline National Memorial (Fig. 3C)/Theodore Roosevelt Area and Cedar Point. The branches of dominant species Quercus virginiana and geminata are characteristically covered with epiphytes Q. and Pleopeltis polypodioides, Tillandsia recurvata, Tillandsia usneoides. Juniperus virginiana, Persea horhonia, common Prunus serotina, and Sahal palmetto are principal understory trees; other tree species are at certain sites: Asimina parvijlora and Sapindus saponaria at Theodore Roosevelt Area, and Carya glahra around Cedar common Point. Callicarpa americana, Ilex vomitoria, Myrica cerijera, Serenoa repens, and Vaccinium spp. are understory shrubs (or shrubby trees); Hamamelis virginiana is also ubiquitous around Fort Caroline. In common the Roosevelt Area, Psychotia nervosa shrub in tropical areas) understory plant but usually (a is a much Woody m) less than 2 ft (0.6 tall. vines are prevalent (i.e., Parthenocissus quinquejolia, Smilax spp., Vitis common aestivalis^ Vitis rotundijolia); herbaceous understory plants include: Bidens hipinnata, Elephantopus nudatus, Galactia Galium hispidulum, Melanthera nivea, Oplismenus hirtellus, Ruellia caroliniensis, Sanicula elliottii, and canadensis, Smallanthus uvedalia, Sporoholus indicus, Vernonia gigantea. — Sandhill Community. Sandhill is characterized by rolling hills of deep, relatively sterile sands inhabited usually by widely spaced oaks and pines with a ground cover of characteristic herbs (and some shrubs). Fire a dominant factor in maintaining this community (FNAI 1990). Sandhill-type associations occur on two is survey sites. The eastern and central portions of the Sohn Purchase is a large area of "scrubby sandhill" (Fig. — 3A), comprisingarelatively dense woody canopy dominated by Quercus geminata with some chapmanni, Q. — and and Pinus taeda various shrubs, including: Gaylussacia spp.. Ilex vomitoria, Lyoniajerruginea, elliottii, P. L. lucida, Myrica cerijera, Serenoa repens, and Vaccinium myrsinites. The sandhill scrub intergrades gradually A with more mesic habitats (swamp to the south; marshland to the northwest). restricted area (ca. 3.7 acres NPS [1.5 ha]), enclosed by the circular driveway of headquarters (Mount Pleasant Road, Fig. 2), is typical longleaf pine-turkey oak sandhill (Pinus palustris-Quercus laevis) also dominated by Q. geminata (Fig. 3B); — Area, Oct 2005) overstory: scattered Pinus polustris and Quercus folcato (background); understory: Serenoa repens (right front) and scattered plants — C hammock of Carphephorus corymbosus (center). Maritime (Fort Caroline National Memorial, Oct 2005) overstory: Quercus virginiana with Vitis rotudifolia vines; understory: Hamamelis virginiana (center), Sanicula canadensis (left foreground), and Serenoa repens (foreground). D. Salt marsh — (Round Marsh, Theodore Roosevelt Area, Oct 2005) tidal creek bounded by Spartina alterniflora (bright green) andJuncusroemerianus (dark grayish green); bordering forest (background):y(/mperu5 virginiana, Quercus virginiana, and Sabalpalmetto. E. Shell midden (Round Marsh, Theodore Roosevelt — Area, Oct 2005) overstory: Juniperus virginiana (left foreground) and Forestiera segregata (background) with Smilax auriculata vines (right front); — ground cover: Eustachys petraea (open area). F. Shell midden substrate (same location as E.) mollusk shell fragments mixed with organic matter. — Swamp G. (Thomas Creek Parcel, Apr 2005) overstory trees with expanding leaves (background): Acerrubrum, Liquidambarstyraciflua, and Nyssa sylvatica var. biflora; understory: Iris hexagona (center), Rubus argutus (left front), and Thelypteris kunthii (right front). Photo credit: W.B. Zomlefer. 1166 Journal of the Botanical Research Institute of Texas 1(2) the sparser shrub layer has most of the species present the Sohn Purchase, with the notable addition of at Common Ceratiola ericoides. understory sandhill plants of these two sites include Andropogon spp., Aristida spicijormis, Balduina angustifolia Berlandiera pumila, Callisia graminea, Carphephorus odoratissimus, Crotalaria , rotundijolia, Eragrostis elliottii, Eryngium aromaticum, Gratiola hispida, Lechea torreyi, Liatris tenuifolia, Licania michauxii, Palafoxiaintegrijolia^ Pityopsis graminijolia, Pteridium aquilinum, Seymeriapectinata, Smilax auriculata, and Stillingia sylvatica, Stylisma patens. — Aquatic open Habitats, This general habitat category designates areas of freshwater, including the surrounding margin of often woody vegetation (FNAI 1990). The survey included several ponds in the Fort Caroline National Memorial/Theodore Roosevelt Area (including Spanish Pond; 4 acres [1.6 ha]); expanses of standing water of marshlands in the Sohn Purchase; and the water-filled borrow pit and dikes of Cedar swamp Creek as well as higher waters bordering the there. Floating aquatic species include: Eichhornia Lemna Limnohium Nymphaea crassipes, Eandoltia punctata, aequinoctialis, spongia, odorata, Sagittariafilijormis, common and Salvinia minima^ emergent wetland plants are: Cladiumjamaicense, Eleocharisflavescens, Gratiola ramosa^ Hypericum mutilum Juncus ejjusus^ Ludwigia spp., Panicum hemitomon, verrucosum, Pluchea rosea, P. , Polygonum spp., Pontederia cordata, Rhynchosporajascicularis, Sagittaria graminea, S. lancijolia, Setariaparvijlora, and Spartina hakeri. Cephalanthus occidentalism Diospyros virginiana, Ilex glabra, Lyoniajruitcosa, Pinus serotina, and Salix caroliniana are often components of the shrubby border of these wetlands. — Swamp Hardwood (Lowland Forest). This habitat occurs in low-lying, periodically flooded areas FNAI (often bordering stream banks); the soil a mixture of clay and organic matter (Ewel 1990; 1990). is Swamp forest is characterized as a closed-canopy of tall deciduous hardwoods with dense shrubby un- derstory. Ferns and herbs also occur in more open areas. The southeastern portion of Thomas Creek has swamp substantial 3G) that intergrades with flatwoods; the mesic hardwoods of the southern Sohn (Fig. hammock Mixed swamp-maritime property gradually transitions into scrubby sandhill. vegetation also surrounds Spanish Pond in the Fort Caroline National Memorial/Theodore Roosevelt Area. The following Thomas many swamp canopy trees are typical for Creek (and also occur at the other sites): Acer ruhrum, Fraxinus caroliniana, Liquidamhar Magnolia virginiana, Nyssa sylvaticavar. Perseapalustris, styraciflua. hiflora, Woody Platanus occidentalis, Quercus laurijolia, Q. nigra, Q. virginiana, and Ulmus americana. understory species include: Carpinus caroliniana. Ilex cassine, Myrica cerijera^ Smilax laurifolia^ Ruhus argutus, and Toxicodendron radicans. Fxamples of herbaceous plants that flourish under open areas of the canopy (often in standing water) include: Boehmeria cylindrica, Carex vulpinoidea, Chasmanthium laxum, Iris hexagona, Juncus ejjusus, Osmunda cinnamomea, Paspalum urvillei, Pontederia cordata, Rhynchospora spp., Saururus cernuus, Thelypteris and Woodwardia kunthii, areolata. — Pine Flatwoods (Mesic Flatwoods; Pine Savannah), ^These relatively areas are characterized flat by poorly drained terrain composed of up 3 m) of sand overlying organic/clayey hardpan that to ft (ca. 1 impedes water percolation, so that this habitat frequently inundated. The overstory an open canopy is is forest of widely spaced pines with understory and a dense ground cover of shrubs and herbaceous little FNAI plants (Abrahamson &t Hartnett 1990; 1990). Like sandhill, pine flatwoods are also maintained by Thomas Disturbed flatwood habitat located in the central portion of the Creek parcel. This logged fire. is swamp hardwood area, once a pine plantation, grades into the lower lying to the south. Pinus taeda (loblolly pine) and (slash pine) are the dominant overstory species. Shrubs, scattered throughout the wetland P. elliottii and also along its margins, include: Bejaria racemosa, Cyrilla racemijlora (not vouchered). Ilex spp., Lyonia lucida, Lyonia ligustrina yri. Joliosijlora (not vouchered), Lyonia mariana, Myrica cerijera, Quercus elliottii, Q. minima, Q. myrtijolia, Rhus copallinum, Serenoa repens, and Vaccinium corymhosum. Shrubby and herbaceous common, Hypericum species of are H. hrachyphyllum, H. Jasciculatum H. gentianoides H. hypericoides, e.g., , H. mutilum, and H. tetrapetalum. The diverse herbaceous flora (many aquatic species in depressions) also includes: Andropogon spp., Balduina unijlora, Bidens mitis, Bigelowia nudata, Carphephorus odoratissimus, El- eocharis spp., Eriocaulon decangulare, Euthamia caroliniana, Fuirena hreviseta, Helianthus angustifolius Juncus , effusus, Lachnanthes caroliana, Lachnocaulon anceps, Liatris spp., Linum medium, Ludwigia spp., Polygala lutea, P. nana, Rhexia alijanus, RhynchosporaJascicularis, Sabatia hrevifolia, Sarracenia minor, Scleria ciliata, Sorghastrum secundum, Typha Utricularia suhulata, and Xyris spp. latifolia,
